Q1. Name
the stage during which chromatids start moving to the opposite poles.
Solution
Anaphase
Q2. Define bivalents.
Solution
Bivalents are the homologous chromosomes which are paired during the
zygotene stage of prophase I in meiosis.
Q3. State
the events which take place during prophase.
Solution
Events which occur during prophase:
Chromosomal material condenses into
chromosomes. Chromatids and centromeres are visible.
The mitotic spindle starts forming in the
cytoplasmic microtubules and proteinaceous components of the cytoplasm.
Q4. Which is the longest phase of the cell cycle?
Solution
Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle.
Q5. Sanjay
observes a cell in the metaphase stage under a microscope. Describe the
structure or appearance of chromosomes which he may have observed.
Solution
Chromosomes are thick and clearly visible.
Their two sister chromatids are visible.
The sister chromatids are held together by the
centromere.
Small disc-shaped structures are visible at the surface of the
centromeres. These structures are called kinetochores, and they provide the
surface of attachment of spindle fibres to chromosomes.
Q6. Distinguish
between the cytokinesis of plant cell and animal cell.
Solution
Cytokinesis of Animal Cell
Cytokinesis of Plant Cell
A
furrow appears in the plasma membrane.
Cytokinesis
begins with the formation of the cell plate in the middle of the cell.
The
furrow deepens and joins the centre dividing the cell into two
daughter cells.
The
cell plate grows from the centre outwards, dividing the cell into two
daughter cells.
Q7. State
the events which occur during interphase.
Solution
Events which occur during the interphase are as follows:
The cells grow.
DNA replication takes place.
Q8. What
does the cell plate represent?
Solution
The cell plate represents the middle lamella between the walls of the
adjacent cells.
Q9. State the duration of the cell cycle in yeast.
Solution
The duration of the cell cycle in yeast is 90 minutes.
Q10. Identify
the stages during which the following events occur in M phase:
Spindle fibres attach to the kinetochores of
chromosomes.
Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum
disappear.
Daughter chromosomes begin their migration
towards the opposite poles.
Centromere splits.
Solution
Q11. Name the following:
Complex structure formed during synapsis
The stage between two meiotic divisions
The sites at which the homologous chromosomes
remain unseparated during prophase I
Enzyme involved in crossing over
Solution
Q12. State
the event which marks the beginning of prophase during mitosis.
Solution
Initiation of condensation of chromatin material marks the beginning
of prophase during mitosis.
Q13. Define the following:
M phase
Interphase
Solution
Q14. Define meiosis.
Solution
Meiosis is a specialised kind of cell division which reduces the
chromosome number by half resulting in the formation of haploid daughter cells.
Q15. Define crossing over.
Solution
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between two
homologous chromosomes.
Q16. Draw a diagram
of the cell cycle indicating the formation of two new daughter cells from the
parent cell.
Solution
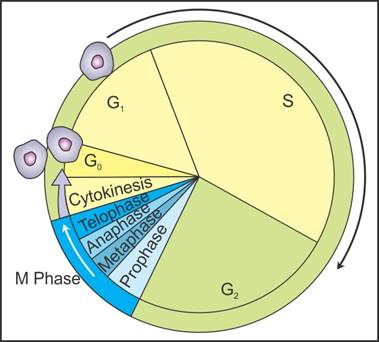
Q17. Define
cell cycle.
Solution
The sequence of events during which a cell duplicates its genome,
synthesises its other constituents and eventually divides into two daughter
cells is called the cell cycle.
Q18. Label
the diagram and also determine the stage at which the contents of a cell
appear like the following diagram.
Solution
Metaphase:
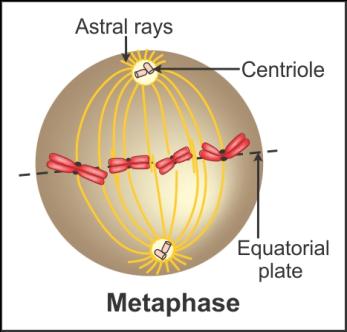

Q19. Name
the stage at which the morphology of chromosomes can be studied.
Solution
The morphology of chromosomes can be studied at metaphase.
Q20. In how
many hours do human cells in a culture divide?
Solution
Human cells in a culture divide every 24 hours.
Q21. Explain the events which occur during a pachytene stage.
Solution
The following events occur during the pachytene stage:
Recombination nodules appear.
Homologous chromosomes cross over at the recombination nodules for the exchange of genetic material.
Q22. Why is
mitosis also called equational division?
Solution
During mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny
cells is the same. Hence, it is also called equational division.
Q23. Distinguish
between interphase and M phase.
Solution
Interphase
M phase
It
the phase between two successive M phases.
It
is the phase during which actual cell division takes place.
It
is the longest phase of the cell cycle.
It
is the short phase of the cell cycle.
Chromosomes
are in the form of chromatin.
Chromosomes
are thick and rod-like.
Q24. State
the two phases of the cell cycle.
Solution
The two phases of the cell cycle are
Interphase
Mitosis phases
Q25. Write the entities which will be missing if a cell at the end of prophase is observed under the microscope.
Solution
If the cell at the end of prophase is observed under a microscope, the Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and nuclear envelope would be missing.
Q26. Describe
the process of cytokinesis in plant cells.
Solution
In plant cells, the precursors of the cell wall,
i.e. the cell plate, are formed in the centre of the cell.
The cell plate grows from the middle of the cell
outwards, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
The cell plate represents the middle lamella between the walls of two
adjacent cells.
Q27. Name the enzyme involved in crossing over.
Solution
Recombinase
Q28. Draw the diagrams of
Transition to metaphase
Anaphase
Solution
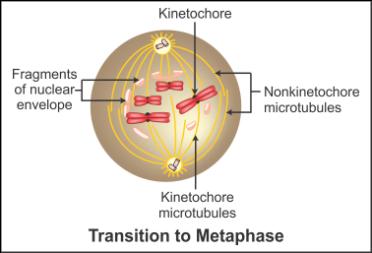
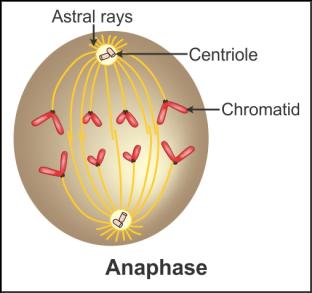
Q29. What are recombination nodules?
Solution
Recombination nodules are the sites at which crossing over occurs
between two non-sister chromatids of the homologous
chromosomes during the pachytene stage.
Q30. Name the cell in which the diplotene phase lasts for years.
Solution
Oocytes of some vertebrates
Q31. State the five phases of meiosis I.
Solution
The five phases of meiosis I are
Leptotene
Zygotene
Pachytene
Diplotene
Diakinesis
Q32. State the significance of fertilisation.
Solution
Fertilisation restores the diploid phase in the life cycle.
Q33. Name
the following:
Division of cytoplasm
Division of nucleus
Solution
Q34. Describe
the quiescent stage of the cell cycle.
Solution
Some cells do not exhibit cell division or some
cells divide only when the body has lost cells during an injury. Such cells
enter the quiescent stage.
In this stage, the cells are metabolically active.
However, the cells do not divide.
They undergo division only when there is a requirement by the body
under certain conditions.
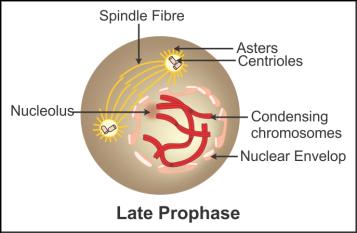
Q35. Identify
the phase shown in the following diagram.
Solution
Late Prophase:

Q36. Write
the three phases which are collectively known as interphase.
Solution
Three phases which are collectively known as the interphase are
G1 phase
S phase
G2 phase
Q37. State the events which occur during the S phase in animal cells.
Solution
During the S phase in animal cells, DNA replicates in the chromosome and centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm.
Q38. How many chromosomes are present in an onion cell?
Solution
14 chromosomes are present in an onion cell.
Q39. What is
the function of kinetochores?
Solution
Kinetochores provide the surface for the attachment of spindle fibres
to the chromosomes.
Q40. State the event which marks the beginning of diakinesis.
Solution
Terminalisation of chiasmata marks the beginning of diakinesis.
Comments
Post a Comment