Q1. Draw the following diagrams:
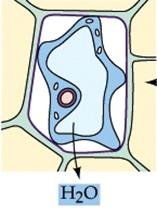
Cell kept in a hypertonic solution
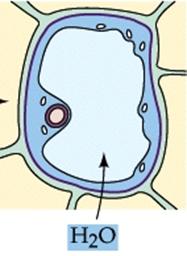
A turgid cell
Solution
Q2. Name the
element which cannot be remobilised.
Solution
Calcium
Q3. Name the
process which utilises energy for the transport of substances.
Solution
Active
transport
Q4. Name the
two complex permanent tissues involved in the transport of substances in
plants.
Solution
Xylem and
phloem the two complex permanent tissues involved in the transport of
substances in plants.
Q5. State the
characteristic features of transport proteins.
Solution
Characteristics
of transport proteins are as follows:
They are selective and specific to the
substances, i.e. each protein will carry only a specific substance
across the membrane.
They are liable to saturate.
They respond to inhibitors.
Their actions are controlled by
hormones.
Q6. Name the
form of carbohydrates which is transported in plants as food.
Solution
Sucrose
Q7. How will
you explain that the phloem is responsible for food transport by an
experiment?
Solution
The phloem
is responsible for food transport. This can be explained by a girdling experiment.
On a tree
trunk, a ring of bark up to a depth of the phloem layer is removed.
Due to
the absence of the phloem layer, the food gets accumulated in the region of
the stem just above the ring.
This
swollen part of the stem indicates that the food is transported through the phloem.
Q8. Represent the relationship between water potential, solute potential and pressure potential.
Solution
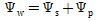
Q9. State the relation between the concentration
of water in a system and its kinetic energy.
Solution
Greater the concentration of water in a
system, higher is its kinetic energy.
Q10. Give two examples of imbibition.
Solution
Two examples of imbibition are as follows:
Absorption of water by seed
Absorption of water by dry wood
Q11. Differentiate
between simple diffusion and active transport.
Solution
Simple
Diffusion
Active
Transport
The movement of molecules is along the
concentration gradient.
The movement of molecules is against the
concentration gradient.
Energy is not required for the transport of
substances.
Energy is used in the form of ATP.
Q12. Write two
similarities between diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
Solution
Q13. Differentiate between hypotonic and
hypertonic solutions.
Solution
Hypotonic Solution
Hypertonic Solution
It has
more water potential than the cytoplasm of the cell.
It has
less water potential than the cytoplasm of the cell.
When
the cell is kept in a hypotonic solution, the cell becomes turgid.
When
the cell is kept in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks.
Q14. When is a solution called a hypertonic
solution?
Solution
When the external solution is more
concentrated than the content of the cytoplasm, a solution is called a hypertonic
solution.
Q15. Distinguish between osmosis and diffusion.
Solution
Osmosis
Diffusion
It is
the movement of solute molecules across a concentration gradient.
It is the
movement of solvent molecules across the concentration gradient.
It does not require any membrane.
It
occurs through a semipermeable membrane.
Q16. Name the
plant tissue system responsible for carrying out long-distance transport of
substances in plants.
Solution
The vascular
plant tissue system is responsible for carrying out long-distance transport
of substances in plants.
Q17. What is the water potential of pure water at
standard temperature?
Solution
At standard temperature, the water potential
of pure water is zero.
Q18. Why is imbibition said to be a type of
diffusion?
Solution
During imbibition, the movement of water
occurs along the concentration gradient; hence, it is said to be a type of
diffusion.
Q19. Name the
process by which sucrose is moved to companion cells and sieve tube cells of the
phloem according to the pressure flow hypothesis.
Solution
Active
transport
Q20. State the names of two components which determine the water potential.
Solution
The components which determine the water potential are as follows:
Solute potential 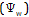
Pressure potential 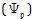
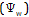
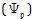
Q21. How much water can a mature plant absorb in a day?
Solution
A mature plant can absorb 3 litres of water in a day.
Q22. Define isotonic solution.
Solution
When the external solution balances the
osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm, the solution is called an isotonic
solution.
Q23. What will happen to the solute potential
inside the cell if the cell is kept in a hypertonic solution?
Solution
If the cell is kept in a hypertonic solution,
then the solute potential inside the cell will increase.
Q24. What are
the components of phloem sap?
Solution
The
components of phloem sap are water and sucrose.
Q25. Explain
the mechanism of the pressure flow hypothesis.
Solution
When
glucose is prepared at the source by photosynthesis, it is converted into
sucrose.
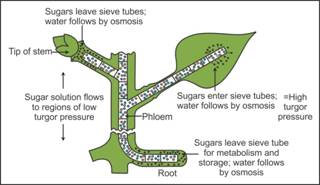 Sucrose
is then transported into the companion cells and then into the phloem sieve
tube cells by active transport. This is called loading of the source.
Loading
creates a hypertonic condition in the phloem due to which water from the adjacent
xylem cells moves into the phloem by osmosis.
As the
osmotic or hydrostatic pressure builds up inside the phloem, the sap moves to
the surrounding areas of the lower osmotic pressure, i.e. the sink.
As the
sucrose moves into the sink, the water potential in the phloem increases
which again moves water into the xylem.
Sucrose
is then transported into the companion cells and then into the phloem sieve
tube cells by active transport. This is called loading of the source.
Loading
creates a hypertonic condition in the phloem due to which water from the adjacent
xylem cells moves into the phloem by osmosis.
As the
osmotic or hydrostatic pressure builds up inside the phloem, the sap moves to
the surrounding areas of the lower osmotic pressure, i.e. the sink.
As the
sucrose moves into the sink, the water potential in the phloem increases
which again moves water into the xylem.
 Sucrose
is then transported into the companion cells and then into the phloem sieve
tube cells by active transport. This is called loading of the source.
Loading
creates a hypertonic condition in the phloem due to which water from the adjacent
xylem cells moves into the phloem by osmosis.
As the
osmotic or hydrostatic pressure builds up inside the phloem, the sap moves to
the surrounding areas of the lower osmotic pressure, i.e. the sink.
As the
sucrose moves into the sink, the water potential in the phloem increases
which again moves water into the xylem.
Sucrose
is then transported into the companion cells and then into the phloem sieve
tube cells by active transport. This is called loading of the source.
Loading
creates a hypertonic condition in the phloem due to which water from the adjacent
xylem cells moves into the phloem by osmosis.
As the
osmotic or hydrostatic pressure builds up inside the phloem, the sap moves to
the surrounding areas of the lower osmotic pressure, i.e. the sink.
As the
sucrose moves into the sink, the water potential in the phloem increases
which again moves water into the xylem.
Q26. In which
region of the plant, the apoplast is absent?
Solution
Apoplast
is absent in the casparian strip of the endodermis in the roots.
Q27. Name the
process by which unloading of minerals occurs in plant cells.
Solution
The
process by which unloading of minerals occurs by plant cells is through
diffusion.
Q28. A raisin was a kept in a bowl containing a
solution for two hours. After two hours, there was increase in the volume and
size of the raisin. Identify the type of solution in which the raisin was
placed.
Solution
Because the raisin swelled up after two
hours, it was kept in a hypotonic solution.
Q29. Name the
vascular tissue which transports sucrose in plants.
Solution
Phloem
transports sucrose in plants.
Q30. What is guttation?
Solution
When the
rate of evaporation is low, at night or in the early morning, excess water
gets collected in the form of droplets at the special openings of veins of
leaves of many herbaceous plants. Such water loss in its liquid phase is
called guttation.
Q31. Define osmotic pressure.
Solution
Osmotic pressure is the pressure developed by
the solute molecules to prevent the inward diffusion of water molecules or
solvent molecules.
Q32. The
direction of movement of food in the phloem can be bidirectional. Justify.
Solution
Usually, the
source is the part of a plant where food is synthesised and the sink is the
part of the plant where the food is required or stored.
However, it
can be reversed, especially during seasonal changes or according to the
plant’s need.
In the
early spring, sugar stored in the roots is sometimes used and acts as a
source, and the buds of trees which need energy for growth and development of
the photosynthetic apparatus act as a sink.
Hence,
the source-sink relationship is variable in plants, and the direction of
movement of food in the phloem is bidirectional.
Q33. Explain
the three physical properties of water which help in the ascent of sap in
plants.
Solution
Properties
of water which help in the movement of ascent of sap are as follows:
Mutual attraction between water molecules.
This property is called cohesion.
Attraction of water molecules to polar
surfaces such as the surface of tracheary elements. This attraction is
also called adhesion.
Water molecules are attracted to each
other more in the liquid phase than in the gas phase. This property is
called the surface tension of water.
All the
above properties help to form a continuous passage of water molecules in the
xylem which moves upwards due to the transpiration pull.
Q34. Distinguish between hypertonic and isotonic
solutions.
Solution
Hypertonic Solution
Isotonic Solution
The
solution does not balance the osmotic pressure of the cell, because its
water potential is lesser than the cytoplasm of the cell.
The
solution balances the osmotic pressure of the cell.
There
is a flow of water outside the cell, and the cell shrinks.
There
is no net flow of water inside or outside, and the cell remains flaccid.
Q35. Differentiate between hypotonic and isotonic
solutions.
Solution
Hypotonic Solution
Isotonic Solution
The
solution does not balance the osmotic pressure of the cell, because its
water potential is greater than the cytoplasm of the cell.
The
solution balances the osmotic pressure of the cell.
There
is a flow of water inside the cell, and the cell swells up.
There is
no net flow of water inside or outside, and the cell remains flaccid.
Q36. How much water can a mustard plant absorb in
5 hours?
Solution
A mustard plant can absorb water equal to its
own weight in five hours.
Q37. What will happen to the pressure potential of
the cell if it is kept in a hypotonic solution?
Solution
If the cell is kept in a hypotonic solution, then
the pressure potential inside the cell will increase.
Q38. Show
diagrammatically symplastic and apoplastic pathways for ion and water
movement in the root hair cells.
Solution
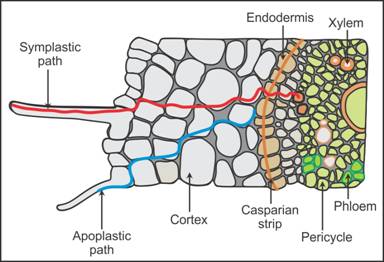
Q39. State the
significance of root pressure.
Solution
Root
pressure helps to re-establish the continuous passage of water molecules in
the xylem.
Q40. Write any one similarity found between enzymes and carrier proteins.
Comments
Post a Comment