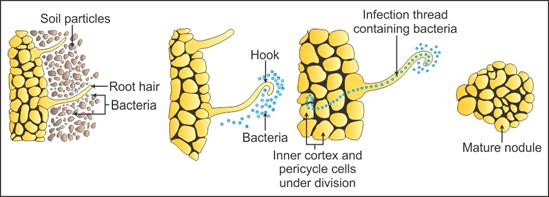
Q1. Represent diagrammatically the development of root nodules in soyabean.
Solution
Development of root nodules in soyabean:

Q2. Name the elements
responsible for delayed flowering.
Solution
Nitrogen,
sulphur and molybdenum
Q3. With the
help of examples explain the role of essential elements in activating or
inhibiting enzymes.
Solution
Magnesium
is an activator for ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase as well as
for phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase.
Both
enzymes play an integral role in CO2 fixation in photosynthesis.
Zinc ions
activate alcohol dehydrogenase and the molybdenum of nitrogenase during
nitrogen fixation.
Q4. Name
parts of the plant where potassium is required in abundant quantities. State
any two functions of potassium ions in plants.
Solution
Potassium
ions are required in the meristematic tissues, buds, leaves and root tips.
Potassium
helps to maintain an anion-cation balance in cells.
Potassium
is required in all phosphorylation reactions.
Q5. Name the compound which when reacts with ammonia forms glutamic aid.
Solution
α-ketoglutaric acid
Q6. Explain
the method of hydroponics.
Solution
In
hydroponics, a series of experiments are conducted in which roots of plants
are immersed in a nutrient solution.
Then an
element is either added or removed or provided in varied concentration in the
solution according to its suitability to the plant and its growth.
Plants
are grown in tubes or troughs placed at a slight incline.
A pump is
provided which circulates the solution from a reservoir to the elevated end
of the tube.
The
solution flows down the tubes and returns back to the reservoir.
The roots
of the plants get bathed continuously in an aerated solution.
Q7. Name the
four categories of essential elements.
Solution
Four
categories of essential elements are as follows:
Components
of biomolecules
Components
of energy-related compounds
Activator
or inhibitor of enzymes
Elements
which alter the osmotic potential of a cell
Q8. Name the
element required for the photolysis of water during photosynthesis.
Solution
Manganous
ions or chlorine ions
Q9. Name the substance present in the middle lamella which contains calcium.
Solution
Calcium pectate
Q10. When is an
element considered toxic for plants?
Solution
Any
mineral concentration which reduces the dry weight of plant tissues by 10% is
toxic for plants.
Q11. State the role of Nitrobacter in nitrogen fixation.
Solution
Nitrobacter oxidises nitrite into nitrate.
Q12. What is the name given to the movement of ions?
Solution
Flux
Q13. Name any
one bacterium which oxidises ammonia to nitrite.
Solution
Nitrosomonas/Nitrococcus
Q14. Excess of
manganese induces deficiency of other elements in plants. Justify.
Solution
Many
times, excess of an element inhibits the uptake of another element by the
plant.
Manganese
when becomes toxic (i.e. present more than its required concentration) causes
brown spots to appear around the chlorotic veins.
Manganese
competes with iron for uptake.
It
competes with magnesium for binding with enzymes.
It inhibits
the calcium translocation in the shoot apex.
Hence,
excess of manganese induces deficiency of other elements in plants.
Q15. Name the
two amino acids which contain sulphur.
Solution
The two
amino acids which contain sulphur are cysteine and methionine.
Q16. State the
quantity of macronutrients required by plants. Name two macronutrients and
micronutrients.
Solution
10 mmol
of macronutrients are required per 1 kg of dry matter.
Examples
of macronutrients are nitrogen and phosphorus.
Examples
of micronutrients are nickel and chlorine.
Q17. Name the elements responsible for the following functions:
Maintenance of the ribosome structure
Activation of catalase
Germination of pollen grains
Photolysis of water
Solution
Q18. Write the chemical equations of the two steps involved in the conversion of ammonia to nitrates.
Solution
Step one: Ammonia to nitrite ions
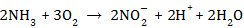 Step two: Nitrites to nitrate ions
Step two: Nitrites to nitrate ions
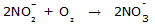
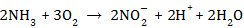 Step two: Nitrites to nitrate ions
Step two: Nitrites to nitrate ions
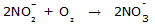
Q19. Name the bacterium which can produce nodules on non-leguminous Alnus.
Solution
Frankia
Q20. Name the
technique of growing plants in a nutrient solution.
Solution
Hydroponics
is the technique of growing plants in a nutrient solution.
Q21. What is
nitrogen fixation? State the two natural sources to provide energy for
nitrogen fixation.
Solution
The
process of conversion of nitrogen to ammonia is called nitrogen fixation.
Ultraviolet radiation and lightning provide energy for nitrogen fixation.
Q22. State the
reason due to which the minerals become available to the roots of plants.
Solution
Weathering
and break down of rocks
Q23. What did Julius von Sachs demonstrate?
Solution
Julius von Sachs demonstrated that plants could be grown in a defined medium in the complete absence of soil and such plants also attain maturity.
Q24. Write any two forms in which nitrogen is taken up by plants.
Solution
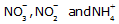 are the forms in which nitrogen is taken up by plants.
are the forms in which nitrogen is taken up by plants.
Q25. Name the
following:
Aerobic
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Anaerobic
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Solution
Q26. Name the
parts of the plants which require potassium ions more abundantly.
Solution
Meristematic
tissues, buds, leaves and root tips require potassium abundantly.
Q27. Describe
the importance of calcium in cell division.
Solution
Calcium
pectate is necessary for the formation of the middle lamella, a part of the cell
wall. Hence, calcium is important in the synthesis of the cell wall during
cell division.
It is
required for the formation of the mitotic spindle.
Q28. Name the
enzyme for which Zn2+ acts as an activator.
Solution
Alcohol
dehydrogenase
Q29. Name the two amides found in plants.
Solution
Asparagine and glutamine
Q30. Draw a well-labelled diagram of a typical setup of nutrient solution culture.
Solution
Typical setup of nutrient solution culture:
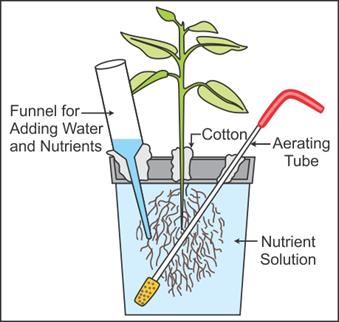

Q31. Name the
vegetables which are produced commercially by using hydroponics.
Solution
Seedless
cucumber, tomato and lettuce
Q32. What is
denitrification? Name the bacteria which perform denitrification.
Solution
Reduction
of nitrate present in the soil into nitrogen is called denitrification.
Bacteria Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus perform denitrification.
Q33. Name the
deficiency symptom in which leaves turn yellow.
Solution
Chlorosis
Q34. Name the elements whose deficiencies are visible in senescent leaves.
Solution
Nitrogen, potassium and magnesium
Q35. Which
element is responsible for the opening and closing of stomata to some extent?
Solution
Potassium
Q36. Name the first phase of uptake of ions in the outer space of cells.
Solution
Apoplast
Q37. State the
criteria which decide the essentiality of elements.
Solution
Criteria which decide the
essentiality of elements:
The
element must be necessary for plant growth and reproduction. In the absence
of such elements, plants do not complete their lifecycles.
The
deficiency of the element cannot be met by supplying some other element.
The
element must be directly involved in plant metabolism.
Q38. Name the element found in plants growing near nuclear testing sites.
Solution
Radioactive Strontium
Q39. Name the minerals present in plant cells which are not released easily.
Solution
Sulphur and calcium
Q40. Name the
element which activates the enzyme nitrogenase during nitrogen metabolism.
Solution
Molybdenum
Comments
Post a Comment