Q1. What are respiratory substances?
Solution
Substances which are oxidised during the process of respiration are
called respiratory substances.
Q2. Name the enzyme which catalyses the conversion of sucrose into glucose
and fructose.
Solution
Invertase
Q3. State the two products formed during glycolysis by the splitting of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. State the relationship between NADH + H+.
Solution
The splitting of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate during glycolysis forms glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
1 NADH + H+is equivalent to three molecules of ATP.
Q4. Name the pathway discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof and J.
Parnas.
Solution
Glycolysis or EMP pathway
Q5. State the factor on
which the respiratory quotient depends.
Solution
The respiratory
quotient depends on the type of respiratory substrate used in respiration.
Q6. State the term used for organisms which feed on dead and decaying
matter.
Solution
Saprophytes
Q7. How many ATP molecules are generated from one pair of hydrogen atoms or one pair of electrons from NADH2?
Solution
3 ATP molecules are generated from one pair of hydrogen atoms
Q8. Name the component which transfers electrons from ubiquinol to cytochrome c.
Solution
Cytochrome bc1 or complex III transfers electrons from ubiquinol to cytochrome c.
Q9. Where does the
electron transport system take place in the mitochondrion?
Solution
The electron
transport system takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Q10. What do you understand by the term cellular respiration?
Solution
The term cellular respiration indicates the oxidation of certain
macromolecules and the breaking of C-C bonds present in these molecules in
the cells to release energy.
Q11. Give the schematic representation of the TCA cycle.
Solution
TCA Cycle:
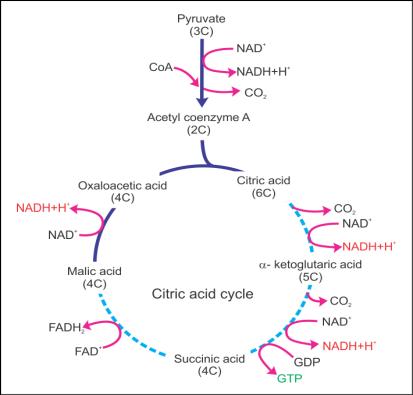

Q12. Write the other
name of complex IV.
Solution
The other name of
complex IV is cytochrome c oxidase complex.
Q13. Write the chemical equations for the Krebs cycle.
Solution
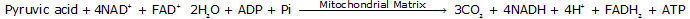
Q14. State the net gain
of ATPs by the oxidation of one glucose molecule.
Solution
38 ATP
Q15. Give the schematic representation of the pathway for anaerobic
respiration.
Solution
Pathway of anaerobic respiration:


Q16. Name the enzymes which catalyse the incomplete oxidation of glucose in yeasts.
Solution
Pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase
Q17. How many molecules of NADH + H+ are formed from one
molecule of glucose?
Solution
Two molecules of NADH + H+are formed from one
molecule of glucose.
Q18. How many molecules of pyruvate are formed from one molecule of glucose?
Solution
Two molecules of pyruvate are formed from one molecule of glucose.
Q19. What is the first step of the TCA cycle?
Solution
The first step of the TCA cycle is the condensation of the acetyl group
of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetic acid and water to obtain citric acid.
Q20. In which form do the
proteins enter the respiration pathway?
Solution
Acetyl CoA
Q21. What will be the RQ if tripalmitin is used as a substrate in respiration?
Solution
0.7
Q22. Write the chemical equation of the complete combustion of glucose during respiration.
Solution
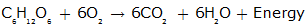
Q23. Name the isomer of glucose-6-phosphate formed during glycolysis.
Solution
Fructose-6-phosphate
Q24. Name the molecule which is synthesised with the help of F0 and F1 particles.
Solution
ATP
Q25. State the
components of complex IV.
Solution
Cytochrome a,
cytochrome a3 and two copper centres are the components of complex
IV.
Q26. Write the chemical equation for the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA.
Solution
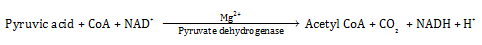
Q27. Draw a flowchart
explaining the interrelationship between the metabolic pathway and the breakdown
of different molecules into CO2 and H2O.
Solution
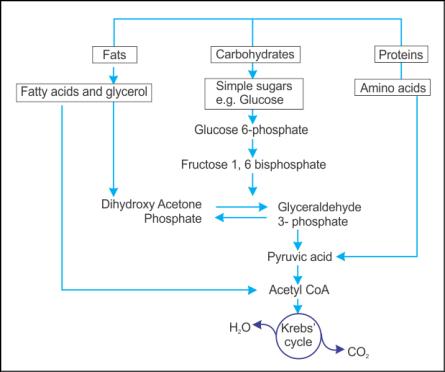
Q28. Name the two products formed by two successive decarboxylations in the
TCA cycle.
Solution
α-ketoglutaric acid and succinyl CoA
Q29. State the site where the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid
takes place.
Solution
Matrix of mitochondrion
Q30. State the net gain of ATP during glycolysis.
Solution
8 molecules of ATP
Q31. How are fats
utilised as substrates in aerobic respiration?
Solution
Fats are first
broken down into glycerol and fatty acids.
Fatty acids are
first degraded to acetyl CoA and then they enter the TCA cycle.
Glycerols are
converted into phosphoglyceraldehyde, and they can then enter the glycolytic
pathway.
Q32. What is the value of RQ in germinating wheat grains?
Solution
Respiratory substrate in germinating wheat grains is carbohydrate. When carbohydrates are completely oxidized, RQ is equal to 1.
Q33. State the site of glycolysis in the cell.
Solution
Cytoplasm
Q34. Give the schematic representation of the EMP pathway (glycolysis).
Solution
EMP Pathway:


Q35. Draw a well-labelled diagram indicating the synthesis of ATP in mitochondria.
Solution
Synthesis of ATP in mitochondria:


Q36. Name the component responsible for the
transfer of electrons between complex III and complex IV.
Solution
Cytochrome c
Q37. Describe the first step of TCA cycle.
Solution
The first step is the condensation step which involves the condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid in presence of water.
Q38. How would proteins enter the respiratory pathway?
Solution
Proteins are first degraded into amino acids by enzyme proteases.
The amino acids either enter the pathway immediately or first get degraded to pyruvate or acetyl CoA.
Q39. What is the significance of Krebs cycle?
Solution
Krebs cycle serves as a common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The end products of glucose and amino acid change to acetyl co-A to enter Krebs cycle whereas β-oxidation of fatty acid produces acetyl co-A as the end product.
β
Q40. Name the substance which is released during the formation of citric
acid in the TCA cycle.
Solution
CoA
Comments
Post a Comment