Q1. Give one example of cells of plants which have
undergone
Dedifferentiation
Redifferentiation
Solution
Q2. Describe arithmetic growth.
Solution
In arithmetic growth following mitotic cell division, only one daughter cell continues to divide while the other daughter cell differentiates and matures.
When arithmetic growth is plotted against time, it gives a linear growth curve.
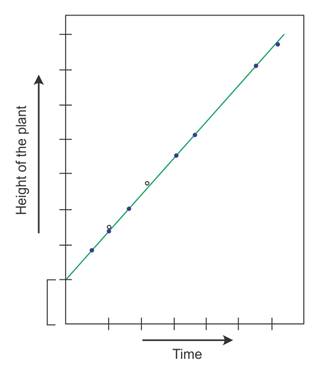 The mathematical expression of arithmetic growth is
Lt = L0 + rt,
where Lt = length at time ‘t’
L0 = length at time zero
r = growth rate
The mathematical expression of arithmetic growth is
Lt = L0 + rt,
where Lt = length at time ‘t’
L0 = length at time zero
r = growth rate
 The mathematical expression of arithmetic growth is
Lt = L0 + rt,
where Lt = length at time ‘t’
L0 = length at time zero
r = growth rate
The mathematical expression of arithmetic growth is
Lt = L0 + rt,
where Lt = length at time ‘t’
L0 = length at time zero
r = growth rate
Q3. What is dedifferentiation? State one example.
Solution
As the cells grow and mature, they lose their
capacity to differentiate. However, under certain conditions, such cells
regain the capacity of division which is called dedifferentiation.
Differentiated parenchymatous cells dedifferentiate
to form interfascicular cambium and cork cambium.
Q4. Name the
compound which is used in agriculture as a source of ethylene.
Solution
Ethephon
Q5. Draw a well-labelled diagram indicating the germination and development of a seed.
Solution
Germination and Development of Seed:
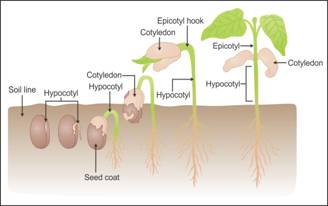

Q6. State the term used for the phenomenon in which the shape of leaves of the same plant changes during its development.
Solution
Heterophylly
Q7. Name any
two parts of the plant which synthesise natural cytokinins.
Solution
Young
fruits, root apices
Q8. Name the
plant growth regulator used in the brewing industry for the malting process.
Solution
Gibberellic acid
Q9. Name the
phenomenon in which a growing apical bud inhibits the growth of the lateral
bud.
Solution
Apical
dominance
Q10. State the
name of the plant growth regulator which you will use in the following cases:
To
promote flowering in pineapples
To
stimulate early seed production in conifers
To
sprout potato tubers
To
prevent leaf drop at an early age
To
prepare weed-free lawns
To
delay leaf senescence
Solution
Q11. Abscisic
acid is also known as stress hormone.
Solution
Abscisic
acid inhibits seed germination. It also stimulates the closure of stomata and
increases the tolerance level in plants against various stresses. Hence, abscisic acid is also known as a stress hormone.
Q12. State one
example of arithmetic growth.
Solution
Elongation
of the root at a constant rate is an example of arithmetic growth.
Q13. State the
parameters which are considered while measuring the growth of plants.
Solution
Parameters
which are considered while measuring the growth of plants are as follows:
Increase
in fresh weight
Increase
in dry weight
Increase
in length of plants
Increase
in area and volume of plants
Increase
in cell number
Q14. Name the
plant and its part from which auxin was isolated by
F. W. Went.
Solution
Tips of
coleoptiles of oat seedlings.
Q15. State the term which explains the ability of plants to respond to the environment or phases of life by following different pathways.
Solution
Plasticity
Q16. Differentiate
between arithmetic and exponential growth.
Solution
Arithmetic
Growth
Geometric
Growth
After mitotic division, only one
daughter cell divides and the other daughter cell differentiates and matures.
All the daughter cells continue
to divide.
On plotting the growth against
time, a linear curve is obtained.
On plotting the growth against
time, a sigmoid curve is obtained.
Q17. How is the quantitative comparison between the growth of living beings done?
Solution
The quantitative comparison between the growth of living beings can be done in two ways:
Absolute growth rate: Measurement and comparison of the total growth per unit time.
Relative growth rate: Growth of the given system per unit time expressed on a common basis.
Q18. Name the
PGR which hastens the ripening of oranges.
Solution
Ethylene
Q19. Name the PGR which is a modified form of adenine.
Solution
Kinetin
Q20. How does ethylene help plants to absorb more water and minerals?
Solution
Ethylene promotes root growth and root hair formation, thus increasing the surface area of absorption which helps plants to absorb more water and minerals.
Q21. State the
functions of cytokinins.
Solution
Functions
of cytokinins:
They help to overcome apical dominance.
They also promote nutrient mobilisation
which results in the delay of leaf senescence.
Q22. From where was auxin isolated first? Name one natural auxin and one synthetic auxin.
Solution
Auxin was first isolated from human urine.
Natural auxin - Indole butyric acid
Synthetic auxin - Naphthalene acetic acid
Q23. Give three examples of dedifferentiation in plants.
Solution
1. Formation of interfacscicular cambium
2. Formation of cork cambium from fully differentiated parenchymatous cells.
3. Formation of callus by culturing the cells of pith during plant tissue culture
Q24. What type
of tissues synthesise ethylene? State any two functions of ethylene.
Solution
Ethylene
is synthesised in tissues which undergo senescence and in ripening fruits.
It
accelerates abscission in flowers and fruits.
It breaks
seed and bud dormancy.
Q25. Name the
fungus which causes the bakanae disease in rice
seedlings.
Solution
Gibberella fujikuroi
Q26. State the characteristics of cells in the elongation phase of the growth of a plant.
Solution
Cells in the elongation phase of the growth of a plant show the following characteristics:
They show increased vacuolation, i.e. more number of vacuoles.
Cells are enlarged.
There is new cell wall deposition.
Q27. What is
open form growth?
Solution
Open form
growth is the growth in which new cells are always added to the plant body by
the activity of meristems.
Q28. Name the
phenomenon which explains the importance of low temperature and flowering in
plants.
Solution
Vernalisation
Q29. Define
growth rate.
Solution
The growth
rate is the increased growth per unit time.
Q30. Define development.
Solution
Development can be defined as all the changes which an
organism goes through during its life cycle.
Q31. Write the
mathematical expression for exponential growth.
Solution
W1
= W0ert
Q32. Define plasticity and give one example.
Or
How can heterophylly be an example of plasticity?
Solution
Plasticity is the ability of plants to respond to
the environment or phases of life or to form different structures by
following different pathways.
Terrestrial plants have different shapes of leaves,
and the leaves of aquatic plants also show different shapes in their life
cycle.

 A coriander leaf in the juvenile stage looks
different from the mature leaf.
A coriander leaf in the juvenile stage looks
different from the mature leaf.
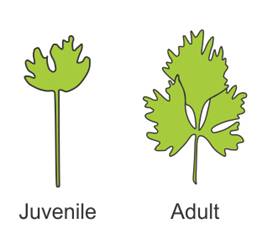

 A coriander leaf in the juvenile stage looks
different from the mature leaf.
A coriander leaf in the juvenile stage looks
different from the mature leaf.

Q33. Name the
three substances which were discovered and later collectively named abscisic acid (ABA).
Solution
Inhibitor
B, abscission II and dormin.
Q34. Define
growth. Give an example of growth in plants.
Solution
Growth is
an irreversible permanent increase in the size of an organ or part or the
individual cell. Expansion of leaves is an example of growth in plants.
Q35. State the
chemical nature of gibberellins.
Solution
Acidic
Q36. State the
three phases of the period of growth in plants, and describe the
characteristic features of the cells of each phase.
Solution
The
period of growth in plants has the following three phases:
Meristematic
phase:
This phase is represented by the root and shoot apices.
The cells of the meristematic region are rich
in protoplasm and possess large conspicuous nuclei.
The cell walls are thin, cellulosic, primary
and show more plasmodesmata connections.
Elongation
phase:
The zone of elongation is proximal to the meristematic zone.
The cells show more number of vacuoles.
Enlargement of cells and new cell wall
deposition occur during this phase.
Maturation:
It lies proximal to the zone of elongation.
The cells of this phase show more
protoplasmic modifications and thickened cell walls.
Q37. Name the
two processes which add to development.
Solution
The two
processes which add to development are growth and differentiation.
Q38. How do gibberellins help in increasing the sugar yield?
Solution
Gibberellins help in stem elongation in plants. In sugarcane, sugar is stored in stems. Use of gibberellin ensures an increase in the stem length of sugarcane; hence, the yield increases.
Q39. Which PGR
acts as an antagonist to gibberellins?
Solution
Abscisic
acid
Q40. Describe
relative growth. Also, plot a graph indicating relative growth.
Solution
In geometric growth, the progeny cells
continue to divide mitotically.
The initial phase, i.e. the lag phase, is
very slow.
After the lag phase, the growth takes place
very rapidly at an exponential rate, which is called the log phase.
Due to limited nutrient supply, the growth
slows down leading to the stationary phase.
When a graph is plotted of the growth rate
against time, we get a sigmoid or S curve.
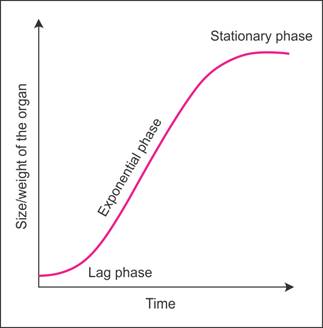 The geometric growth rate is expressed as
W1 = W0ert,
where W1 = final size (weight,
height, number etc.)
W0
= initial size at the beginning of the period
r =
growth rate
t = time of growth
e =
base of natural logarithm
The geometric growth rate is expressed as
W1 = W0ert,
where W1 = final size (weight,
height, number etc.)
W0
= initial size at the beginning of the period
r =
growth rate
t = time of growth
e =
base of natural logarithm
 The geometric growth rate is expressed as
W1 = W0ert,
where W1 = final size (weight,
height, number etc.)
W0
= initial size at the beginning of the period
r =
growth rate
t = time of growth
e =
base of natural logarithm
The geometric growth rate is expressed as
W1 = W0ert,
where W1 = final size (weight,
height, number etc.)
W0
= initial size at the beginning of the period
r =
growth rate
t = time of growth
e =
base of natural logarithm
Comments
Post a Comment