Q1. Where does the chemical process of digestion begin?
Solution
Oral cavity
Q2. What is assimilation?
Solution
Assimilation is the use of absorbed food or nutrients by the tissues.
Q3. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the human stomach.
Solution
Human stomach:


Q4. Explain diphyodont dentition.
Solution
Dentition in which animals exhibit two kinds of teeth in their life - first
deciduous teeth and second adult teeth - is called diphyodont dentition.
Q5. Name the capsule which covers the hepatic lobule.
Solution
Glisson’s capsule
Q6. Name the physiological process by
which complex food substances are converted into simple food substances.
Solution
Digestion
Q7. Name the movements which help to pass the food down through the oesophagus.
Solution
Peristalsis
Q8. Explain the process of emulsification.
Solution
Because fatty acids are insoluble, they are not absorbed in the blood easily. They are first broken down into small fat droplets called micelles.
Micelles are further moved into mucosa, where they are formed into small protein-coated fat globules called chylomicrons.
Chylomicrons are then absorbed by the lacteal lymph vessels of villi.
Q9. Name the gland present in the lower jaw.
Solution
Sub-maxillary gland
Q10. What is succus entericus? State its role.
Solution
The mucus secreted by the goblet cells of the intestinal mucosal
epithelium and the secretions of the brush border cells of mucosa are together
called succus entericus. Enzymes present in the succus entericus act on the
products formed during digestion, i.e. dipeptides, disaccharides,
monoglycerides and nucleosides, to form simple absorbable products.
Q11. Name the two ducts which form the bile duct.
Solution
The cystic duct and the hepatic duct join to form the common bile duct.
Q12. Name the three regions of the stomach.
Solution
The three regions of the stomach are cardiac, fundus and pylorus.
Q13. Why are humans called heterodonts?
Solution
Human beings show the presence of four types of teeth, i.e. canines,
incisors, molars and premolars. Hence, they are called heterodonts.
Q14. Name the enzyme which digests milk proteins in infants.
Solution
Rennin
Q15. Name the lymph vessel which joins villi.
Solution
Lacteal vessel
Q16. Name the bile pigments present in bile.
Solution
Bilirubin and biliverdin
Q17. What is the optimal pH for pepsin in the stomach?
Solution
1.8 is the optimal pH for pepsins.
Q18. Draw an outline of the human digestive system. Label any ten parts.
Solution
Human digestive system:
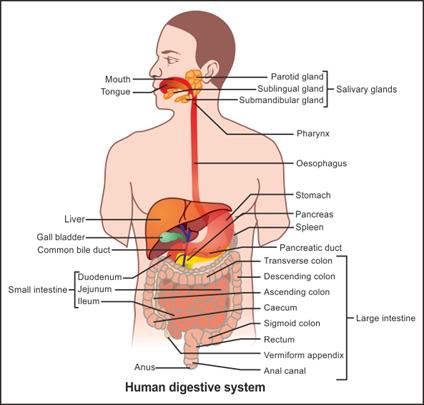 (Label any ten parts)
(Label any ten parts)
 (Label any ten parts)
(Label any ten parts)
Q19. Draw the diagrams of
Section of the small intestine
Arrangement of teeth human
Solution
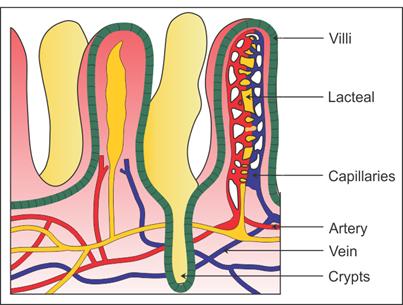

Q20. State the term used for the protein-coated fat droplets.
Solution
Chylomicrons
Q21. State the role of lysozyme present in the saliva.
Solution
Lysozyme acts as an anti-bacterial agent and prevents infections.
Q22. State the action of the following enzymes and the resulting end-product:
Carboxypeptidase
Sucrase
Nucleosidases
Amylase
Solution
Q23. Name the cells which secrete HCl in the stomach.
Solution
Oxyntic cells
Q24. Write any two causes of indigestion.
Solution
Inadequate enzyme secretion and anxiety
Q25. Write any five reactions which occur in the duodenum.
Solution
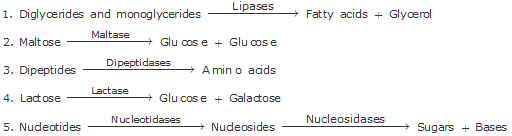
Q26. Name the region of the large intestine where symbiotic microorganisms
take their shelter.
Solution
Caecum
Q27. What is the technical term used for temporary milk teeth?
Solution
Deciduous teeth
Q28. Name the vestigial organ which is part of the human digestive system.
Solution
Vermiform appendix
Q29. Name various substances present in bile. State the functions of bile.
Solution
Various substances present in bile are bilirubin, biliverdin, bile
salts, cholesterol and phospholipids.
Bile helps in breaking down of the fats into small micelles, and this
process is called emulsification. Bile also helps in activation of lipases.
Q30. Explain the role of the buccal cavity during digestion.
Solution
The buccal cavity performs mastication of food and facilitates swallowing.
The teeth and tongue mix the food thoroughly with saliva.
The mucus present in the saliva helps in lubricating food, and it also
adheres masticated food particles together into a bolus.
The bolus is then swallowed and conveyed into the pharynx.
Q31. Name the enzyme of pancreatic juice which acts on nucleic acids.
Solution
Nuclease
Q32. State the percentage of the total starch which gets hydrolysed in the mouth.
Solution
30%
Q33. Name the enzymes present in the saliva.
Solution
Salivary amylase and lysozyme
Q34. What is the function of the gastro-oesophageal sphincter?
Solution
The gastro-oesophageal sphincter regulates the opening of the oesophagus into the stomach.
Q35. What are partially hydrolysed proteins called?
Solution
Peptones
Q36. Name three secretions released into the small intestine.
Solution
Bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice
Q37. Explain the process of the removal of undigested waste from the body.
Solution
The undigested material or waste first gets solidified into the coherent faeces and is stored in the rectum.
It initiates the neural reflex which causes an urge for its removal.
The defaecation or egestion of waste occurs through the anal opening by the mass peristaltic movements of the anal muscles which is a voluntary process.
Q38. State the role of the large intestine.
Solution
Role of the large intestine:
Water is absorbed in the large intestine,
and drugs and minerals are also absorbed to some extent.
The large intestine secretes mucus which
helps in adhering undigested particles together and lubricates them for
an easy passage outside the body.
Q39. Where do you find the sphincter of Oddi?
Solution
The sphincter of Oddi is situated between the opening of the
hepatopancreatic duct and the duodenum.
Q40. Name the structure which secretes inactive trypsinogen. How is trypsinogen activated?
Solution
Trypsinogen is secreted by the pancreas. An enzyme called enterokinase which is secreted by the intestinal mucosa activates trypsinogen.
Comments
Post a Comment