Q1. Name the disorder in which glucose is present in excess quantities in
urine.
Solution
Glycosuria
Q2. Name the branch of the renal artery which enters the glomerulus.
Solution
Afferent arteriole
Q3. Name the excretory organs found in the following organisms:
Earthworm
Liver fluke
Prawns
Cockroach
Solution
Animal
Excretory Organs
Earthworm
Nephridia
Liver
fluke
Flame cells
Prawns
Green/antennal glands
Cockroach
Malpighian tubules
Q4. What activates the release of vasopressin from the neurohypophysis?
Solution
Excessive loss of body fluid activates the release of vasopressin from the neurohypophysis.
Q5. Name the three layers through which blood is filtered during glomerular filtration.
Solution
Layers through which blood filters during glomerular filtration are
Endothelium of glomerular blood vessels
Epithelium of Bowman’s capsule
Basement membrane present between the endothelium of the glomerulus and the epithelium of Bowman’s capsule
Q6. What are ammonotelic animals? Give any two examples.
Solution
Animals which excrete nitrogenous waste products in the form of
ammonia are called ammonotelic animals.
Examples: Bony fish, aquatic insects
Q7. Name the three factors which activate the osmoreceptors in our body.
Solution
Three factors which activate the osmoreceptors in our body are
Blood volume
Body fluid volume
Ionic concentration
Q8. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the renal corpuscle.
Solution
Renal corpuscle:
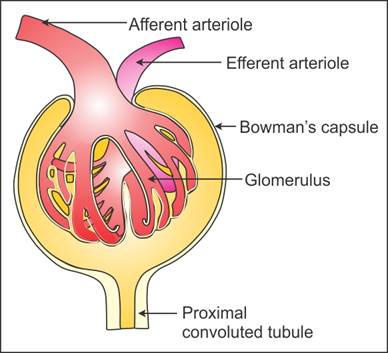

Q9. Describe the structure of the Malpighian body.
Solution
The Malpighian body constitutes the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule.
The glomerulus is a tuft of blood capillaries.
The afferent arteriole enters the glomerulus, while the efferent
arteriole leaves the glomerulus.
The Bowman’s capsule is a cup-shaped structure.
The glomerulus is situated in the cup-shaped depression of the
Bowman’s capsule.
Q10. State the function of rennin.
Solution
Renin stimulates the glomerular blood flow to bring the glomerular
filtration rate back to normal.
Q11. Distinguish between uricotelism and ureotelism.
Solution
Uricotelism
Ureotelism
Waste products are excreted in the form of uric acid.
Waste products are excreted in the form of urea.
Elimination of uric acid requires less amount of water.
Elimination of uric acid requires moderate amount of water.
It is the least toxic substance.
It is a moderately toxic substance.
Reptiles, birds, insects and land snails exhibit uricotelism.
Marine fish, mammals and terrestrial amphibians exhibit ureotelism.
Q12. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the human urinary system.
Solution
Human urinary system:
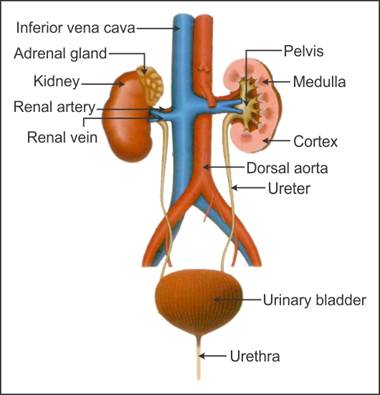

Q13. Name the notch present on the inner concave surface of the kidney.
Solution
Hilum
Q14. Name the part of the nephron which is situated in the medulla of the kidney.
Solution
Henle’s loop
Q15. Name the excretory organ of Planaria.
Solution
Flame cells
Q16. State in one line as to what happens in following disorders:
Renal calculi
Glomerulonephritis
Solution
Q17. Where do you find the slit pores in the Bowman’s capsule?
Solution
Slit pores are present between the podocytes in Bowman’s capsule.
Q18. Name the hormones which play a crucial role in regulating the function
of kidneys.
Solution
Renin, vasopressin, atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) and angiotensin I
Q19. Explain the renin-angiotensin mechanism.
Solution
A fall in glomerular blood pressure activates the juxta glomerular cells to release renin.
Renin converts angiotensin, first to angiotensin I and then to angiotensin II.
Angiotensin II increases the glomerular blood pressure which increases the glomerular filtrate rate (GFR).
At the same time, angiotensin II activates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
Aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of sodium ions and water from DCT. This also results in an increase in GFR.
Q20. How is urea formed in ureotelic animals?
Solution
In ureotelic animals, ammonia is converted into urea in the liver.
The urea formed is then released into the blood from where it is
filtered and excreted by the kidneys.
Q21. Name any two substances present in the sebum.
Solution
Sterols and wax
Q22. Explain micturition.
Solution
The process of release of urine is called micturition.
When the urinary bladder gets filled with urine, the stretch receptors
present on the walls of the bladder send signals to the central nervous
system (CNS).
In response to these signals, CNS sends the motor message which causes
the contraction of smooth muscles of the bladder and simultaneous relaxation
of the urethral sphincters. This results in the release of urine from the
body.
Q23. Name the neural mechanism responsible for micturition.
Solution
Micturition reflex
Q24. How is kidney stone formed?
Solution
Kidney stone is formed by the precipitation of uric acid and accumulation of oxalate crystals.
Q25. Name the network of the efferent arteriole formed around the renal
tubule.
Solution
Peritubular capillaries
Q26. What is the significance of the hilum in the kidneys?
Solution
Ureters, blood vessels and nerves enter the kidneys at the hilum.
Q27. Explain how the glomerular filtration rate is maintained by the kidneys?
Solution
Maintenance of the glomerular filtration rate is carried out by the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidneys.
It is the region formed by the close contact between the distal convoluted tubule and the afferent arteriole at a region.
When GFR falls, it stimulates JGA to release rennin.
Renin helps to bring reduced GFR back to normal.
Q28. What is uraemia? Name and describe the process used to remove waste
substances from individuals suffering from uraemia.
Solution
Uraemia is the accumulation of urea in the blood due to malfunctioning
of the kidneys.
In individuals suffering from uraemia, the waste substances are
removed by haemodialysis.
In this process, blood is drained from the convenient artery (usually
radial artery), mixed with anticoagulant such as heparin and pumped into the
dialysing unit.
The dialysing unit consists of a coiled tube surrounded by a dialysing
fluid.
The dialysing unit has the same composition as that of the plasma
membrane, but it does not contain any nitrogenous waste.
The absence of nitrogenous water in the dialysing unit enables the
easy movement of waste from urine into the tube through the porous membrane,
thus clearing the blood from any waste.
The cleared blood is then pumped back into the body through the same
vein after adding anti-heparin.
Q29. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the L. S. of kidney. Label any six
parts.
Solution
L. S. of kidney:
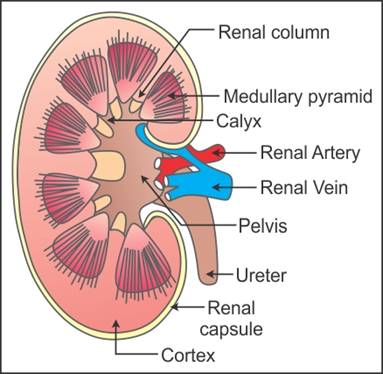

Q30. Apart from the collection of the urine formed, what are the other
functions performed by the collecting duct?
Solution
The collecting duct at times absorbs a large amount of water to
produce concentrated urine.
It allows some amount of urea to enter the medullary interstitium to
maintain osmolarity.
It secretes hydrogen and potassium ions to maintain pH and ionic
balance of the blood.
Q31. State the function of sebum.
Solution
The sebum provides a protective oily covering which protects the skin.
Q32. Name the anticoagulant which is usually used in the haemodialysis process.
Solution
Heparin
Q33. A parrot and a dog were fed only a protein-rich diet. In what forms
would they excrete nitrogenous wastes?
Solution
The parrot will excrete uric acid, while the dog will excrete urea.
Q34. Distinguish between ammonotelism and uricotelism.
Solution
Ammonotelism
Uricotelism
Waste
products are excreted in the form of ammonia.
Waste
products are excreted in the form of uric acid.
Elimination
of ammonia requires more water.
Elimination
of uric acid requires less amount of water.
Aquatic
amphibians, bony fish and aquatic insects exhibit ammonotelism.
Reptiles,
birds, insects and land snails exhibit uricotelism.
Q35. Identify the regions of the renal tubules which absorb the following substances:
Urea, water, HCO3−, K+
Solution
Urea
Collecting duct
Water
Proximal convoluted tubule
HCO3−
Proximal convoluted tubule
K+
Proximal convoluted tubule
Q36. Name the excretory organs in fish.
Solution
Body surface and gills
Q37. State the function of protonephridia in amphioxus.
Solution
Protonephridia in amphioxus maintain the ionic and fluid volume, i.e. protonephridia play an important role in osmoregulation.
Q38. State the role of Henle’s loop in urine formation.
Solution
Henle’s loop maintains high osmolarity of the medullary interstitial fluid.
Q39. Name any two classes of uricotelic animals of the phylum Chordata.
Solution
Reptiles and birds
Q40. State the location of kidneys in the human body.
Solution
The kidneys are situated between the levels of the last thoracic and
third lumbar vertebrae close to the dorsal inner wall of the abdominal
cavity.
Comments
Post a Comment