Q1. Write any two distinguishing characters of dinoflagellates.
Solution
1)Dinoflagellates have stiff plates of cellulose on the outer surface.
2)Their rapid multiplication gives a red appearance to the sea which is known as red tides.
Q2. Draw a well-labelled diagram of Nostoc.
Solution
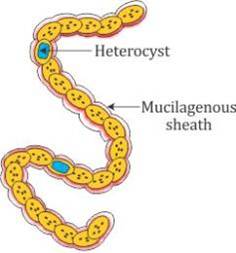
Q3. What is Plasmodium?
Solution
Plasmodium is the aggregation of slime moulds which grow and spread on a large area over several feet under suitable conditions.
Q4. What is mycorrhiza?
Solution
Mycorrhiza is the symbioant association of fungi with the roots of higher plants.
Q5. What are chemosynthetic bacteria? State their importance.
Solution
Chemosynthetic bacteria oxidise substances such as ammonia, nitrites and nitrates and use the released energy for the synthesis of ATP.
Chemosynthetic bacteria help in recycling nutrients such as phosphorus, nitrogen, sulphur, iron etc.
Q6. What are lichens?
Solution
Lichens are a mutually useful symbiotic association between algae and fungi.
Q7. Name the protein-rich layer in Euglena which replaces the cell wall.
Solution
Pellicle
Q8. Name the organisms which were placed under kingdom Plantae before the five kingdom classification. Why?
Solution
Bacteria, cyanobacteria, fungi, mosses, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms were placed in kingdom Plantae because these organisms possess a cell wall.
Q9. Define plasmogamy.
Solution
Plasmogamy is the fusion of protoplasms of motile or non-motile gametes.
Q10. Why are deuteromycetes called imperfect fungi?
Solution
Only asexual and vegetative phases of deuteromycetes are known; hence, they are called imperfect fungi.
Q11. To which kingdom do bacteria belong?
Solution
Bacteria belong to kingdom Monera.
Q12. What is the name of the
fully formed virus particle?
Solution
The name of the fully
formed virus particle is called virion.
Q13. Write a short note on Cyanobacteria.
Solution
Cyanobacteria:
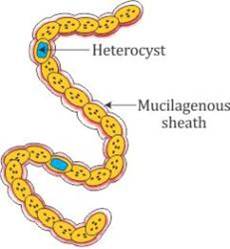 They are also called blue-green algae.
They are unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
They are found in fresh or marine water. Some of them are also terrestrial.
They show the presence of rigid cell walls.
In motile cyanobacteria, flagellum is present.
Cyanobacteria are photoautotrophs and show the presence of chlorophyll a.
Cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts.
Anabaena and Nostoc are examples of cyanobacteria.
They are also called blue-green algae.
They are unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
They are found in fresh or marine water. Some of them are also terrestrial.
They show the presence of rigid cell walls.
In motile cyanobacteria, flagellum is present.
Cyanobacteria are photoautotrophs and show the presence of chlorophyll a.
Cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts.
Anabaena and Nostoc are examples of cyanobacteria.
 They are also called blue-green algae.
They are unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
They are found in fresh or marine water. Some of them are also terrestrial.
They show the presence of rigid cell walls.
In motile cyanobacteria, flagellum is present.
Cyanobacteria are photoautotrophs and show the presence of chlorophyll a.
Cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts.
Anabaena and Nostoc are examples of cyanobacteria.
They are also called blue-green algae.
They are unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
They are found in fresh or marine water. Some of them are also terrestrial.
They show the presence of rigid cell walls.
In motile cyanobacteria, flagellum is present.
Cyanobacteria are photoautotrophs and show the presence of chlorophyll a.
Cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts.
Anabaena and Nostoc are examples of cyanobacteria.
Q14. Explain the terms mycobiont and phycobiont.
Solution
Mycobiont is the fungal component of a lichen which provides shelter and absorbs minerals and water for the algae.
Phycobiont is the algal component of lichen which prepares food for fungi.
Q15. How is a viroid different from a virus?
Solution
A viroid lacks the protein coat which is present in a virus.
Q16. Give any two examples of insectivorous plants.
Solution
Bladderwort, Venus fly trap
Q17. Name any one disease caused by viroids.
Solution
Potato spindle tuber disease is caused by viroids.
Q18. Give two examples of cyanobacteria.
Solution
Nostoc
Anabaena
Q19. A virus is considered a
living organism and an obligate parasite when inside a host cell. However, a virus
is not classified along with bacteria or fungi. What are the characters of a virus
which are similar to non-living objects?
Solution
The
characters showing that viruses are non-living:
They do not show cellular
metabolism and lack respiration.
They have no proper cellular
structure.
They are active only when
they are inside the living host cells.
Q20. A virus is considered as a living organism and an obligate parasite when inside a host cell. However, a virus is not classified along with bacteria or fungi. What are the characters of a virus which are similar to non-living objects?
Solution
Characterisics of virus similar to non-living objects are as follows:
Viruses do not have any specific cellular structure.
They do not have their own metabolism.
They show absence of growth.
Irritability is absent.
They can be crystallised.
Q21. What is diatomaceous earth?
Solution
The accumulation of large amounts of cell wall deposits left back by diatoms over billions of years is called diatomaceous earth.
Q22. Name the group of fungi which are also known as sac fungi.
Solution
Ascomycetes
Q23. What are the criteria used to classify fungi in different classes?
Solution
Criteria used to classify fungi in different classes:
1. Morphology of the mycelium
2. Mode of spore formation and fruiting bodies
Q24. Draw a labelled diagram of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV).
Solution
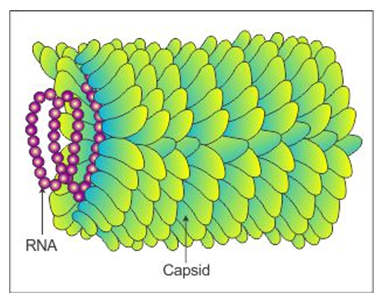
Q25. Write the name of fungi which is used extensively in genetic work.
Solution
Neurospora
Q26. Who proposed the five kingdom classification?
Solution
R. H. Whittaker proposed the five kingdom classification.
Q27. Explain genetic material in viruses.
Solution
Viruses contain either RNA or DNA as genetic material.
The genetic material of a virus is infectious.
Viruses which infect plants have single-stranded RNA.
Viruses which infect animals have either single-stranded or double-stranded RNA or double-stranded DNA.
Bacteriophages have double-stranded DNA.
Q28. Explain the steps of the sexual cycle of fungi.
Solution
The sexual cycle of fungi occurs in three steps:
1.Plasmogamy: Protoplasms of two motile or non-motile gametes fuse.
2.Karyogamy: Fusion of nuclei of two gametes.
3.The zygote undergoes meiosis resulting in the formation of haploid spores.
Q29. Explain the alternation of generation in plants.
Solution
Alternation of generation is observed in plants. Plants show two phases in their life cycle—the diploid sporophyte phase and the haploid gametophyte phase—which alternate with each other.
Q30. Write any two features of spores of slime moulds.
Solution
Features of slime moulds:
1)Spores survive for many years under adverse conditions.
2)They possess true cell walls.
Q31. Explain the groups of protozoa.
Solution
There are four groups of protozoa:
1. Amoeboid Protozoans:
Amoeboid protozoans live in fresh or sea water or in moist soil.
They have pseudopodia to capture their prey. The body surface of marine amoeboid protozoans is covered with silica shells.
Examples: Amoeba, Entamoeba
2. Flagellated Protozoans:
Flagellated protozoans are either free-living or parasitic.
Parasitic forms cause certain diseases such as sleeping sickness.
These protozoans have flagella for locomotion.
3. Ciliated Protozoans:
These protozoans have numerous cilia on their body. Because of the cilia, they are actively moving organisms.
Cilia help in locomotion and allow food laden water to enter the organism’s body.
These organisms are aquatic.
Examples: Paramecium
4. Sporozoans:
These protozoans have an infectious spore stage in their life cycle.
They are parasites.
Example: Plasmodium (which causes malaria)
Q32. Describe the three groups of archaebacteria.
Solution
The three groups of archaebacteria are
1. Methanogens: Methanogens grow in marshy areas and in the stomach of ruminants.
Methanogens are responsible for the production of biogas from animal dung.
2. Halophiles inhabit extreme salty areas.
3. Thermoacidophiles inhabit areas which are acidic and rich in sulphur with high temperature. They are mostly found in hot springs.
Q33. What are coenocytic hyphae?
Solution
Hyphae which are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm are called coenocytic hyphae.
Q34. Write about the contributions of the following scientists:
M. W. Beijerinck
W. M. Stanley
Solution
Q35. Describe the formation of haploid spores in fungi.
Solution
In sexually reproducing fungi, hyphae of two compatible mating types fuse.
In some fungi, the fusion of haploid cells immediately forms diploid cells (2n), but in some ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, the fusion results in an n+n stage, i.e. single cell with two nuclei. Such a condition of cell is called the dikaryon condition and the stage is known as dikaryophase.
The polar nuclei of the cells then fuse, and the cell becomes diploid.
Reduction division occurs inside the fruiting bodies resulting in the formation of fungi.
Q36. Write any two features of viroids.
Solution
Features of viroids:
A viroid is a free RNA of low molecular weight.
It lacks a protein coat which is found in viruses.
Q37. Draw a labelled diagram of a bacteriophage.
Solution
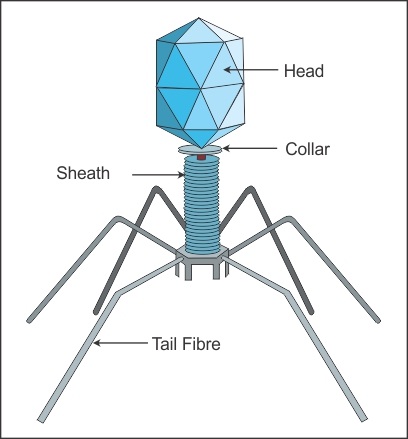
Q38. Name the RNA particle
causing symptoms like those of a virus.
Solution
An RNA particle causing
symptoms like those of a virus is called a viroid.
Q39. Give one example of flagellate protozoan.
Solution
Trypanosoma
Q40. Write the names of the five kingdoms proposed by Whittaker.
Solution
The five kingdoms proposed by Whittaker are Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
Comments
Post a Comment