Q1. Name the two parts of the human body which are connected to each other through the Eustachian tube.
Solution
The cavities of the middle ear and the pharynx are connected to each other through the Eustachian tube.
Q2. What is corpora quadrigemina?
Solution
Corpora quadrigemina is the collection
of four round lobes which represent the dorsal portion of the midbrain.
Q3. Name the gap which exists between
pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurons.
Solution
Synaptic cleft
Q4. Name the pigment present in the
photopigments.
Solution
Opsin
Q5. Draw a well-labelled diagram to explain
the transmission of the nerve impulse at a synapse.
Solution
Transmission of nerve impulse at synapse:


Q6. Eyes are the most important sense organs
in animals without which it would have been difficult to experience the
beauty of life.
Name
the photoreceptor cells and their pigments present in the retina.
Name
the compounds present in the photopigments.
State
the functions of rods and cones.
What
values do you learn from questions (a) and (c)?
Solution
Q7. Name the two photoreceptor cells present
in the eye.
Solution
Rods and cones
Q8. Differentiate between aqueous chamber
and vitreous chamber.
Solution
Aqueous Chamber
Vitreous Chamber
It
is the space between the cornea and the lens.
It
is the space between the lens and the retina.
It
is filled with a fluid called the aqueous humour.
It
is filled with the vitreous humour.
Q9. Name the visible coloured portion of the
eye.
Solution
Iris
Q10. Name the three cells present in the retina of the eye.
Solution
Three cells present in the retina of the eye are ganglion cells, bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells.
Q11. Describe the structure of a neuron.
Solution
Structure of neuron:
Neuron is composed of cell body,
dendrites and axon.
The cell body contains cytoplasm. The cytoplasm
consists of Nissl’s granules which are also present in dendrites.
Dendrites are the short cytoplasmic
branches given out by the cell body. Dendrites carry nerve impulse towards
the cell body.
Axon is the longest process given out by
the cell body.
In case of myelinated neuron, axon is
covered with a myelinated sheath formed by Schwann cells.
The gap between the two adjacent
myelinated regions is called Node of Ranvier.
The distal end of the axon called axon-terminal
has bulb like structures call synaptic knobs which contain neurotransmitters.
Q12. What are nodes of Ranvier?
Solution
Nodes of Ranvier are the gaps present
between the two adjacent myelinated sheaths of the myelinated nerve fibres.
Q13. Apart from the skull, name the covering which protects the brain. Write the names of the three layers which form this protective covering.
Solution
Cranial meninges.
It is made of the following three layers:
Outer dura mater
Middle arachnoid
Inner pia mater
Q14. State the function of the crista ampullaris and the macula.
Solution
The crista ampullaris and the macula are responsible for maintaining body balance and posture.
Q15. State the three types of neurons on the
basis of number of axons and dendrites present. Also, state the number of
axons and dendrites present and their location in the neural system.
Solution
The three types of neurons on the basis
of number of axons and dendrites are
Multi-polar
neuron
Bipolar
neuron
Unipolar
neuron
Multi-polar
neuron: It has one
axon and two or more dendrites. It is found in the cerebral cortex.
Bipolar neuron:It has one axon and one dendrite. It is found
in the retina of the eye.
Unipolar neuron: It has a cell body with only one axon. It is
found during embryonic development.
Q16. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Solution
Neuron:
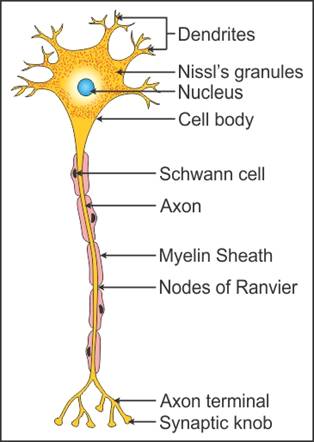

Q17. Define
coordination in living organisms. Why is it necessary? Give any one example.
Solution
Coordination
is the process in which one or more tissues or organs interact and complement
the function of each other to maintain the homeostasis of the body.
During
physical exercise, there is always increased energy demand. To fulfil this
demand, the supply of oxygen to the cells in concern increases. To provide
more oxygen, our respiration rate, heartbeat and blood flow increase.
Q18. Name the ions to which the axonal
membrane is more permeable during the resting potential.
Solution
Potassium ions
Q19. Name the layer of cranial meninges which
is in direct contact with the brain tissue.
Solution
Pia mater
Q20. How many sodium ions move outwards per
two potassium ions during the conduction of nerve impulse?
Solution
Three sodium ions
Q21. State the significance of the cone
cells.
Solution
Cone cells are responsible for colour
vision and photopic vision.
Q22. Write any two points of difference
between the middle layer and the inner layer of the eye.
Solution
Middle layer of eye (Choroid)
Inner layer of eye (Retina)
Blood
vessels are present.
Blood
vessels are absent.
Iris,
lens and pupil belong to the choroid layer.
Contain
rod and cone cells.
Iris,
lens and pupil help light rays to focus on the eye and enter the eye.
Retina
is responsible for the formation of images.
Q23. State the locations of the following:
Vitreous
humour
Bipolar
cells
Solution
Q24. Where are the non-myelinated neurons present in the neural system?
Solution
Autonomic and somatic neural systems
Q25. Name the granular bodies present in the
cytoplasm of neurons.
Solution
Nissl’s granules
Q26. What is the significance of the corpus
callosum?
Solution
The corpus callosum connects the two
cerebral hemispheres.
Q27. What is the other name for the ear drum?
Solution
The other name for the ear drum is tympanic
membrane.
Q28. Name the two parts which form the outer ear.
Solution
Pinna and external auditory meatus form the outer or external ear.
Q29. Name the three ossicles present in the
ear.
Solution
Three ossicles present in the ear are
malleus, incus and stapes.
Q30. At the action potential, what charge is
present on the inner surface of the axonal membrane?
Solution
Positive charge
Q31. To what colours of light do the photopigments respond?
Solution
Photopigments respond to green, red and blue light.
Q32. Name the space between the cornea and
the lens.
Solution
Aqueous chamber
Q33. Which types of neurons are found in the
retina of the eye?
Solution
Bipolar neurons
Q34. Name the pigment spot present at the posterior pole of the eye.
Solution
Macula lutea
Q35. Name the photosensitive compounds
present in the photopigments.
Solution
The photosensitive compounds present in
the photopigments are
Opsin - a protein and retinal (an
aldehyde of vitamin A).
Q36. What are the two nerve fibres of PNS?
Solution
The two nerve fibres of PNS are
Afferent
fibres
Efferent
fibres
Q37. What causes the change in the structure
of opsin?
Solution
Light induced dissociation of retinal
causes change in the structure of opsin.
Q38. Name the external layer of the eyeball.
Solution
Sclera
Q39. Name the structure which connects the
middle ear and the pharynx. Also state its function.
Solution
The Eustachian tube connects the middle
ear and the pharynx. It equalises the pressure on either side of the tympanic
membrane or the ear drum.
Q40. Where are the eyes located?
Solution
Eyes are located in socket-like
structures called orbits of the skull.
Comments
Post a Comment