Q1. Name the following receptors:
Receptors present on the membranes of cells
Receptors present inside the target cell
Solution
Q2. In summer, the urine is more concentrated and thick. Why?
Solution
Vasopressin is responsible for the reabsorption
of water and electrolytes by the distal tubules, and it reduces the loss of
water through urine.
In summer, the secretion of vasopressin increases which helps the body
to conserve more water. Hence, the urine is more concentrated and thick in
summer.
Q3. Name the hormone which
stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and bile juice.
Solution
Cholecystokinin
(CCK)
Q4. Categorise the following hormones according to their chemical nature:
Cortisol, epinephrine, triiodothyronine, gonadotropin-releasing
hormone, FSH
Solution
Cortisol - Steroid
Epinephrine - Amino-acid derivative
Triiodothyronine - Iodothyronine
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone - Peptide hormone
FSH - Peptide hormone
Q5. Which hormone do β-cells secrete?
Solution
Insulin
Q6. Give examples where melatonin regulates the 24-hour rhythm of an organism’s
body.
Solution
Q7. Name the three layers of adrenal cortex.
Solution
The three layers of the adrenal cortex are
Zona reticularis
Zona fasciculata
Zona glomerulosa
Q8. Differentiate between glycogenolysis and glycogenesis.
Solution
Glycogenolysis
Glycogenesis
It
is the process of breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
It
is the process of conversion of glucose into glycogen.
Glucagon
initiates the process.
Insulin
initiates glycogenesis.
It
increases the blood sugar level.
It
decreases or brings back the blood sugar level to normal.
Q9. Name the hormones which are collectively known as gonadotropins.
Solution
Luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Q10. Name the basal part of the diencephalon.
Solution
Hypothalamus
Q11. Show the mechanism of action of FSH.
Solution
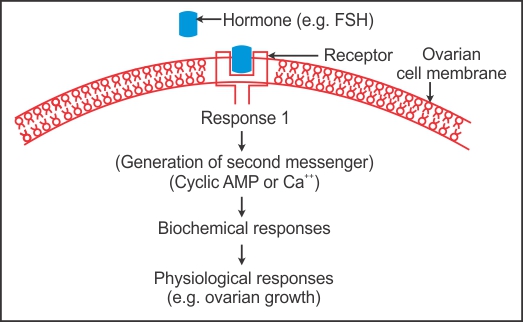
Q12. Write the names of the two regions which together constitute the adenohypophysis.
Solution
Pars distalis and pars intermedia together constitute the adenohypophysis.
Q13. What are ductless glands called?
Solution
Ductless glands are called endocrine glands.
Q14. Name the part which connects the two lobes of the thyroid gland.
Solution
Isthmus
Q15. State the significance of cortisols in the human body.
Solution
Significance of glucocorticoids in the human body:
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis,
proteolysis and lipolysis.
They also inhibit the cellular uptake and use
of amino acids.
Cortisol maintains cardiovascular and kidney
functions.
Cortisol also produces anti-inflammatory
reactions and suppresses the immune response.
It also stimulates the production of red blood
cells.
Q16. State the functions of thyroid hormones.
Solution
Functions of thyroid hormones:
They support the process of red blood cell
formation.
They regulate the basal metabolic rate.
They control the metabolism of carbohydrates,
proteins and fats.
They influence the maintenance of water and
electrolyte balance in the body.
They secrete thyrocalcitonin which regulates the
blood calcium level.
Q17. What are hormone receptors?
Solution
Hormone receptors are the proteins present on target tissues to which
hormones bind to produce their effect on target tissues.
Q18. Name the elements necessary for the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Solution
Iodine
Q19. Name the cell which secretes glucagon.
Solution
α-cells
Q20. Ajay had participated in a running race. He was excited and stood
first in the race.
When he finished the race, his heart was beating fast, and he was
breathing heavily with a lot of sweat.
What could be the reason for these changes in him after the race?
Solution
When Ajay started running, his body experienced a lot of stress.
In response to the stress, the adrenal medulla secreted two hormones
epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Secretion of these hormones resulted in sweating, increased heart
beat, increased respiration, piloerection etc.
Q21. Name the disorder caused by hyposecretion of insulin.
Solution
Diabetes mellitus
Q22. Write the other two names used for the posterior pituitary.
Solution
Neurohypophysis and pars nervosa
Q23. Name the sac in which the testes are located.
Solution
Scrotal sac or scrotum
Q24. Name any two
peptide hormones secreted by the walls of the GI tract.
Solution
Secretin and
cholecystokinin (CCK)
Q25. What is the role of
growth factors in the human body?
Solution
Growth factors are
necessary for the normal growth of tissues and the repairing and regeneration
of cells.
Q26. Explain how the testes play a role in the development of secondary
sexual characters in males? State the secondary sexual characters which are
developed in males.
Solution
Testes also act as endocrine glands and secrete androgens, especially
testosterone.
Secondary sexual characters which develop in males are
Low pitch of voice
Growth of facial and axial hair
Muscular growth
Aggressiveness
Q27. Describe the effects of hypothyroidism on pregnant women.
Solution
Effects of hypothyroidism on pregnant women:
Hypothyroidism causes defective development and
maturation of a growing baby resulting in cretinism.
It also results in mental retardation, low
intelligence, abnormal skin and deaf-mutism.
Q28. How is the
secretion of the parathyroid hormone regulated?
Solution
The circulating
calcium ions in blood regulate the secretion of the parathyroid hormone.
Q29. State the functions of oestrogen.
Solution
Functions of oestrogen:
It stimulates the growth and activities of
secondary sex organs in females.
It stimulates the development of the ovarian
follicle.
It is responsible for the development of
secondary sexual characters such as high pitch voice and the development
of breasts in females.
It regulates female sexual behaviour.
It also promotes the development of mammary
glands.
(Write any three)
Q30. State the two kinds of islets of Langerhans present in the pancreas.
Solution
Two kinds of islets of Langerhans present in the pancreas are α-cells
and β-cells.
Q31. Name the two components of the testis. State the effects of
testosterone on the central nervous system and in carbohydrate metabolism.
Solution
The testis is composed of seminiferous tubules and interstitial
tissue.
Testosterone acts on the central nervous system to influence libido
and male behaviour.
It produces anabolic effect on carbohydrate metabolism.
Q32. State the functions of oxytocin.
Solution
Functions of oxytocin:
Stimulates the contraction of smooth muscles.
It causes the contraction of uterine muscles at
the time of parturition (childbirth).
It is also responsible for milk ejection from the
mammary glands.
Q33. Describe the secretions of endocrine glands in one sentence.
Solution
Secretions of the endocrine glands are hormones which are non-nutrient
chemicals which act as intercellular messengers and are produced in trace
amounts.
Q34. Name the two systems which jointly coordinate the physiological
functions of the body.
Solution
The nervous system and the endocrine system
Q35. Represent diagrammatically the adrenal gland and its sections showing
the layers of tissues.
Solution
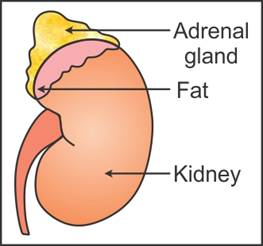
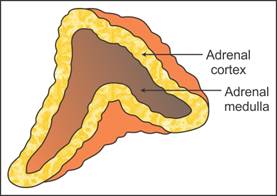
Q36. State the functions of progesterone in females.
Solution
Functions of progesterone in females:
Progesterone supports pregnancy.
It acts on mammary glands and stimulates milk
secretion.
It also promotes the development of sac-like
structures in mammary glands to store milk.
Q37. Which is the main glucocorticoid found in the human body?
Solution
Cortisol
Q38. Name the hormone
secreted by the atrial walls of the human heart.
Solution
Atrial natriuretic
factor (ANF)
Q39. State the function of mineralocorticoids.
Solution
Mineralocorticoids help in maintaining the balance of water and
electrolytes in the body.
Q40. Name the hormone secreted by the corpus luteum.
Solution
Progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum.
Comments
Post a Comment