Q1. Define the
following terms:
1. Isogamous
fusion
2.
Anisogamous fusion
3. Oogamous fusion
Solution
1. Isogamous fusion: Fusion between two gametes of
similar size is called isogamous fusion.
2. Anisogamous fusion: Fusion between two gametes
which are dissimilar in size is called anisogamous fusion.
3. Oogamous fusion: Fusion between one large,
non-motile female gamete and a smaller, motile male gamete is called oogamous
fusion.
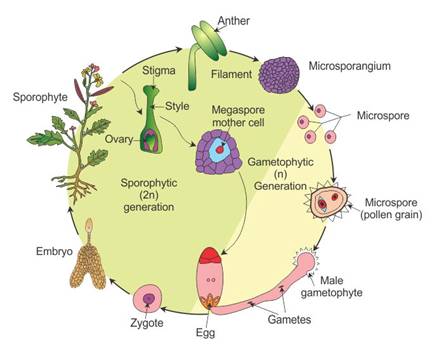
Q2. Draw a labelled diagram of the lifecycle of an angiosperm.
Solution
Lifecycle of an angiosperm:

Q3. What are sporophylls?
Solution
Sporophylls are leaf-like appendages in pteridophytes which bear
sporangia.
Q4. What is anisogamous fusion?
Solution
Anisogamous fusion is the fusion between two gametes which are
dissimilar in size.
Q5. Name the process by which haploid spores are produced by the
sporophyte.
Solution
Meiosis
Q6. Name an alga which shows the diplontic life cycle.
Solution
Fucus
Q7. Give any two examples of pteridophytes in which sporophylls are in the form of strobili.
Solution
Selaginella, Equisetum
Q8. State the uses of algae
Solution
Uses of algae:
Algae help to increase the level of dissolved
oxygen in their immediate environment.
Species of algae such as Porphyra, Laminaria
and Sargassum are used as food.
Hydrocolloids produced by algin and carrageen
are used commercially.
Commercial product agar is obtained from
certain species of algae.
Examples: Gelidium
and Gracilaria
Agar is used in the preparation of ice creams
and jellies. It is also used to grow microbes in laboratories.
Species such as Chlorella and Spirulina are
rich in proteins and thus used as food supplements.
Q9. State the dominant phase in the life cycle of fern.
Solution
The sporophytic phase is the dominant phase in the life cycle of fern.
Q10. Which plant group
produces spores and embryos but lacks vascular tissues and seeds?
Solution
Bryophytes consist of a thalloid body and are
attached by hair-like structures called rhizoids. These lack vascular tissue
and require water at the time of fertilisation. The haploid gametophyte
(formation of spores for sexual reproduction) alternates with the diploid
sporophyte (formation of spores for asexual reproduction).
Q11. Name the dominant phase in a plant with a haplontic life cycle.
Solution
The gametophyte is the dominant phase in a plant with a haplontic life
cycle.
Q12. State any two important features of dicotyledons.
Solution
Important features of dicotyledons:
Seeds of dicotyledons show two cotyledons.
Leaves of dicotyledons show reticulate
venation.
Vascular bundles are arranged in concentric
circles.
Q13. What are microsporangia or male strobili?
Solution
Microsporangia are the strobili which bear microsporophylls and
microsporangia in gymnosperms.
Q14. What are macrosporangia or female strobili?
Solution
Macrosporangia are cones which bear megasporophylls containing ovules or megasporangia in gymnosperms.
Q15. State any one feature of conifers which helps to reduce water loss.
Solution
Presence of sunken stomata.
Q16. Write the name of the species of moss which provides peat?
Solution
Sphagnum
Q17. In plants, haploid as well as diploid cells undergo mitosis. Hence,
during the life cycle of a sexually reproducing plant, there is an
alternation of generation between gametophyte and sporophyte.
Name the dominant phase seen in the life cycle
of gymnosperms.
Name three types of life cycles shown by the
plants.
What is the difference between the life cycles
of bryophytes and pteridophytes?
What value do you learn from the life cycles of
plants?
Solution
Q18. Write the components of the cell wall of Rhodophyceae and Phaeophyceae.
Solution
Group of algae
Components of cell wall
Rhodophyceae
Cellulose, pectin and polysulphate esters
Phaeophyceae
Cellulose and algin
Q19. Give any two examples of plants which exhibit a haplontic life cycle.
Solution
Chlamydomonas and Spirogyra
Q20. Write any two differences between Chlorophyceae and Rhodophyceae.
Solution
Chlorophyceae
Rhodophyceae
1. Food is stored in the form of pyrenoids.
1. Food is stored in the form of floridean starch.
2. Chlorophyll a and b are present.
2. Red pigment called r-phycoerythrin is present.
Q21. What does a pollen chamber in a gymnosperm represents?
Solution
In gymnosperms, the pollen chamber represents a cavity in the ovule in which pollen grains are stored after pollination.
Q22. What is the
unique feature of bryophytes?
Solution
The main plant body of
bryophytes is gametophytic which is independent and may be thallose or
foliose. The sporophyte is differentiated into foot, seta and capsule and is
partially or fully dependent on the gametophyte.
Q23. Write the pigments found in members of the Phaeophyceae group of
algae.
Solution
Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll c, carotenoids and xanthophyll
(fucoxanthin).
Q24. Multicellular
branched rhizoids and leafy gametophytes are characteristics of which group?
Solution
In pteridophytes, the gametophyte
generation is reduced and the sporophyte is well developed. In bryophytes, the
gametophyte constitutes the well-developed generation, but it is foliose in
mosses.
Q25. Explain the
modes of reproduction in Ulothrix.
Solution
In Ulothrix,
reproduction may occur by the following methods:
1. Vegetative
reproduction by fragmentation or by formation of different types of spores.
2. Asexual
reproduction by flagellated zoospores.
3. Sexual
reproduction by the isogamous, anisogamous or oogamous fusion of gametes.
Q26. Describe the plant body of brown algae.
Solution
The
plant body of brown algae is attached to the substratum by a holdfast.
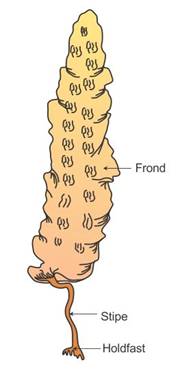 It has
a stalk called stipe.
The frond is a leaf-like photosynthetic organ of the plant body.
It has
a stalk called stipe.
The frond is a leaf-like photosynthetic organ of the plant body.
 It has
a stalk called stipe.
The frond is a leaf-like photosynthetic organ of the plant body.
It has
a stalk called stipe.
The frond is a leaf-like photosynthetic organ of the plant body.
Q27. Distinguish between monocotyledons and dicotyledons.
Solution
Monocotyledons
Dicotyledons
1. Seeds have single cotyledon.
1. Seeds have two cotyledons.
2. Leaves show parallel venation.
2. Leaves show reticulate venation.
Q28. Which plant is commonly known as maiden hair fern?
Solution
Adiantum is commonly known as maiden
hair fern.
Q29. Why are bryophytes called amphibians of the plant kingdom?
Solution
Bryophytes can live in soil, but they are dependent on water for
sexual reproduction; therefore, they are called amphibians of the plant
kingdom.
Q30. What is protonema?
Solution
Protonema is the first stage in the gametophytic phase of a moss.
Q31. Describe the events which occur during the life cycle of an angiosperm.
Solution
During pollination, the pollen grains germinate on the stigma.
This results in the formation of pollen tube which grows through the style and reaches the ovule.
When the pollen tube enters the sac, two male gametes are discharged.
One male gamete fuses with the egg cell and forms a zygote.
The second male gamete fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus and produces the triploid primary endosperm nucleus (PEN).
Because the fusion occurs twice, it is called double fertilisation.
The zygote develops into an embryo, while the primary endosperm nucleus develops into endosperm.
The endosperm provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
The synergids and antipodals of the egg apparatus degenerate after fertilisation.
At the end of this cycle, ovules develop into seeds which give rise to a new plant (sporophyte) while ovaries develop into fruits.
Q32. Name the pigment present in the members of Rhodophyceae.
Solution
R-phycoerythrin
Q33. Name the diploid phase in the plant with a haplontic life cycle.
Solution
The zygote is the diploid phase in a plant with a haplontic life cycle.
Q34. Describe the structure of the vegetative cell of Chlorophyceae.
Solution
The vegetative cell has a cell wall made of cellulose.
The cell wall is covered with a gelatinous coating of algin.
The protoplast of vegetative cells contains plastids, vacuole and nucleus.
Q35. Write important characteristics of gymnosperms.
Solution
Characteristics of Gymnosperms:
Ovules are not covered by ovary.
Seeds are naked.
Gymnosperms exhibit a tap root system.
Gymnosperms are heterosporous.
(Write any 3)
Q36. Define flower.
Solution
A flower is a special reproductive structure in angiosperms in which
the pollen grains and ovules develop.
Q37. Define pollination.
Solution
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains, after their dispersal,
from the anthers to the stigma of the pistil of the same flower or different
flower of the same species.
Q38. Where are the sex organs produced in the plant body of moss?
Solution
In moss, the sex organs are produced at the apex of leafy shoots.
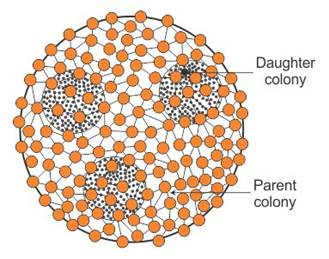
Q39. Draw diagrams of a) Volvox b) Chara
Solution
a) Volvox:
 b) Chara:
b) Chara:
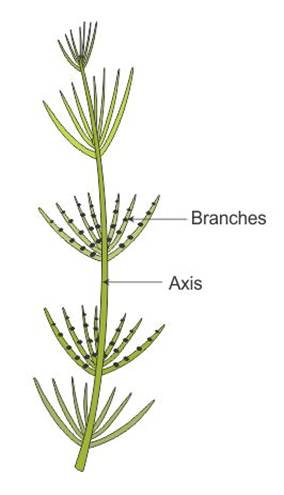
 b) Chara:
b) Chara:

Q40. Distinguish between haplontic and diplontic life cycles.
Solution
Haplontic Life Cycle
Diplontic Life Cycle
Gametophytic phase is dominant.
Sporophytic phase is dominant.
Sporophyte is in the form of a diploid zygote.
Gametophyte is single celled or few celled.
Comments
Post a Comment