Q1. State similarities between phyla
Arthropoda and Mollusca.
Solution
Similarities between phyla Arthropoda
and Mollusca:
They are triploblastic animals.
They are bilaterally symmetrical animals.
They are coelomates.
They exhibit organ system level of
organisation.
Q2. Write the scientific name of the freshwater sponge.
Solution
Spongilla
Q3. Name
the flatworm which has high regeneration capacity.
Solution
Planaria possesses high regeneration capacity.
Q4. Describe
symmetry in animals.
Solution
Animals can be categorised on the basis of their symmetry pattern.
They can be categorised as follows:
Asymmetrical animals
Bilaterally symmetrical animals
Radially symmetrical animals
Asymmetrical animals: The body of these animals
cannot be divided into two identical halves along any plane passing
through the centre. Example: Sponges
Bilaterally symmetrical animals: The body can
be divided into identical left and right halves in only one plane.
Examples: Arthropods, annelids
Radially symmetrical animals: The body of these
animals can be divided into equal halves by any plane passing through
the central axis of the body. Example: Adult echinoderms
Q5. Name the cells which line the spongocoel in Sycon.
Solution
Pinacocytes line the spongocoel in Sycon.
Q6. Differentiate between Annelida and
Arthropoda.
Solution
Annelida
Arthropoda
1) Body is externally divided into
ring-like metameres.
1) Body is divided into head, thorax
and abdomen.
2) Annelids show the presence of a
closed circulatory system.
2) Arthropods show the presence of
an open circulatory system.
3) Locomotion is by chaetae or
parapodia.
3) Locomotion is by jointed
appendages and/or wings.
4) Excretion occurs by nephridia.
4) Excretion occurs by Malpighian
tubules.
Q7. What is the importance of pneumatic bones and air sacs in Aves?
Solution
Pneumatic bones in Aves keep the animal body light and hence help in flight. Air sacs in birds help in respiration and buoyancy.
Q8. What are setae?
Solution
Tiny chitinous bodies in the skin of annelids are termed as setae.
Q9. State the function of comb plates in comb jellies.
Solution
Comb plates found in comb jellies help in
locomotion.
Q10. Enlist the characteristic features of Petromyzon as representative of class Cyclostomata.
Solution
Characteristic features of Petromyzon:
It is
an ectoparasite.
The
body is elongated bearing 6-15 pairs of gills.
The
mouth is circular, sucking type with jaws.
Cranium
and vertebral column are cartilaginous.
It
has a closed circulatory system.
Although
it is marine, it migrates to freshwater for
spawning.
Q11. State different respiratory organs of
animals of phylum Arthropoda.
Solution
Respiratory organs of phylum
Arthropoda: book lungs, gills and book gills.
Q12. Draw a well-labelled diagram of cnidoblast.
Solution

Q13. What is the organ of sound production in Aves. Give its location.
Solution
Syrinx is the organ of sound production in birds. It is located at the bifurcation of trachea into bronchi.
Q14. Write
any two examples of phylum Platyhelminthes.
Solution
Examples of phylum Platyhelminthes: Taenia, Fasciola hepatica
Q15. Write any two examples of phylum Hemichordata.
Solution
Examples of phylum hemichordate: Balanoglossus, Saccoglossus
Q16. Name the excretory organ of
Balanoglossus.
Solution
Proboscis gland
Q17. What is ovovivipary?
Solution
Development of heavily yolked eggs in the mother's reproductive tract without drawing nourishment from her is called ovovivipary.
Q18. Draw a well-labelled diagram of Balanoglossus.
Solution

Q19. What are amniotes?
Solution
Reptiles, birds and mammals that form special embryonic membranes during development are called amniotes. The special embryonic membranes include amnion, chorion, allantois and yolk sac.
Q20. How is the phylum Annelida named?
Solution
In annelids, the body surface is distinctly marked into ring-like segments. This is a distinct and common feature seen in all animals which belong to this phylum. Hence, it is named as phylum Annelida. In Latin, annulus means little ring.
Q21. Write
characteristic features of phylum Platyhelminthes.
Solution
Characteristic features of phylum Platyhelminthes:
They are bilaterally symmetrical.
They do not have any body cavity; hence, they
are acoelomates.
They are triploblastic animals.
Excretion and osmoregulation occur by
specialised cells called flame cells.
Fertilisation is internal.
(Write any 3 or 4)
Q22. Name the organ which regulates buoyancy in Rohu.
Solution
The air bladder regulates buoyancy in Rohu.
Q23. How are the animals of Arthropoda
different from those of Mollusca?
Solution
Arthropoda
Mollusca
1) Body is segmented and divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
1) Body is soft, unsegmented
and divided into head, muscular foot and visceral mass.
2) Excretion is by Malpighian tubules.
2) Excretion is by gills or
kidneys.
3) Respiration is by gills, tracheal tubes or book lungs.
3) Respiration is by gills.
4) Arthropods have chitinous exoskeleton.
4) Molluscs have calcareous
exoskeleton.
Q24. Draw diagrams representing the germinal layers found in diploblastic and triploblastic animals.
Solution
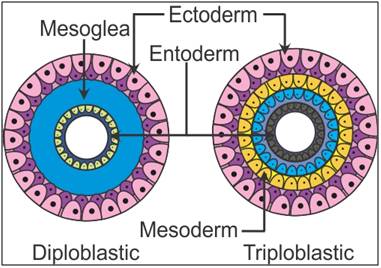
Q25. State
any two phyla of non-chordates which have radial symmetry as their
characteristic feature.
Solution
Animals from the phyla Cnidaria and Echinodermata show radial
symmetry.
Q26. Name the cnidarian which exhibits alteration of generation.
Solution
Obelia exists in both forms, i.e. polyp and medusa, and it shows alteration of generation.
Q27. Name the fish which has an electric organ.
Solution
Torpedo
Q28. Why is Ascaris also
called roundworm?
Solution
The cross-section of the body of Ascaris
appears circular. Hence, Ascaris is
also called roundworm.
Q29. Distinguish between Porifera and Ctenophora
Solution
Porifera
Ctenophora
Animals
show cellular level of organisation.
Animals
show tissue level of organisation.
They
are asymmetrical.
They
are radially symmetrical.
Digestion
is intracellular.
Digestion
is extracellular and intracellular.
Fertilisation
is internal.
Fertilisation
is external.
Example:
Sycon
Example:
Pleurobrachia
Q30. Define
metamerism.
Solution
Metamerism
is a kind of segmentation in which the body is segmented externally and
internally. The external segments of the body correspond to the internal
segments.
Q31. Given below are the pairs of animals and phylum which they belong to. Which out of these is not a matching pair and why?
Bombyx - Arthropoda
Loligo - Mollusca
Asterias - Mollusca
Saccoglossus - Hemichordata
Solution
The pair Asterias - Mollusca is not matching.
Asteria, i.e. star fish, shows the presence of a water vascular system, the adult is radially symmetrical and larvae are bilaterally symmetrical. Hence, Asterias is an echinoderm.
Q32. Name the parts of which the body of Balanoglossus
is composed of.
Solution
The body of Balanoglossus is composed
of an anterior part proboscis, a collar and a long trunk.
Q33. What kind of body cavity do the arthropods and nematodes have?
Solution
Arthropods have blood-filled haemocoel and nematodes have fluid-filled pseudocoel.
Q34. State the criteria which form the basis of classification of the animal kingdom.
Solution
Criteria which form the basis of classification of animal kingdom are
Level of organisation of cells: Some animals show cell-level organisation, some tissue-level and some exhibit organ-level organisation of cells.
Body symmetry: Asymmetrical, bilaterally symmetrical and radially symmetrical.
Nature of coelom: Coelomates, acoelomates and pseudocoelomates.
Presence or absence of notochord: Chordates and non-chordates.
Number of embryonic layers found in animals: Diploblastic and triploblastic conditions.
Segmentation of the body.
Q35. Mention three characters of a spider in which it differs from an insect.
Solution
1. Body divisions such as cephalothorax and abdomen
2. Lack of antennae and wings
3. Four pairs of legs
Q36. Name the compound present in the skeleton of corals.
Solution
Calcium carbonate is found in the skeleton of
corals.
Q37. Distinguish between diploblastic and triploblastic animals.
Solution
Diploblastic Animals
Triploblastic Animals
The cells are arranged in two embryonic layers—external ectoderm and internal endoderm.
The cells are arranged in two embryonic layers—external ectoderm, middle layer of mesoderm and internal endoderm.
Mesoglea is present between the ectoderm and the endoderm.
Mesoglea is absent. Instead, the mesoderm is present between the endoderm and the ectoderm.
Examples: Cnidaria and Ctenophora
Examples: Platyhelminthes to Chordata
Q38. Why are the animals which belong to phylum Platyhelminthes called flatworms?
Solution
The animals of phylum Platyhelminthes have their bodies dorsoventrally flattened. Because they appear flat, they are called flatworms.
Q39. Describe the skeleton of poriferans in one line.
Solution
The skeleton of poriferans is made up of spicules or spongin fibres.
Q40. What is
a true coelom?
Solution
A true coelom is one which is completely lined by amesoderm.
Comments
Post a Comment