Q1. State the name of connective tissues.
Solution
The various connective tissues are cartilage, bone, blood and adipose
tissue.
Q2. Identify the type of epithelium:
(a) Single layer of tall and slender cells
(b) Unicellular columnar cells specialised in secretion
Solution
(a) Single layer of tall and slender cells - Columnar epithelium
(b) Unicellular columnar cells specialised in secretion - Unicellular
glandular epithelium
Q3. Describe the structure and working of heart in cockroach.
Solution
The heart of a cockroach is a long muscular tube
lying along the mid-dorsal line of the thorax and abdomen.
It is differentiated into funnel-shaped chambers,
and it bears ostia on either side.
Blood from the sinuses enters the heart through
ostia, and it moves anteriorly in the heart and is released into the sinuses
again.
Q4. How many Malpighian tubules are present in cockroach?
Solution
100-150 Malpighian tubules are present in cockroach.
Q5. State the locations of the following:
A pair of testes
Male gonopore
Accessory reproductive gland
Sperms
Solution
Q6. What is mesorchium?
Solution
Mesorchium is the double fold of peritoneum through which a pair of
testes is adhered to the upper part of the kidneys in frogs.
Q7. How many ganglia are present in the abdomen of cockroach?
Solution
Six ganglia are present in the abdomen of cockroach.
Q8. What are the favourable conditions required for laying oothecae?
Solution
Oothecae are glued to a suitable surface such as
crevices or cracks.
They require high humidity and a food source.
Q9. What is a phallomere?
Solution
Phallomere is a chitinous asymmetrical structure which acts as the
external male genitalia which surrounds the male gonopore.
Q10. Name the fibrils present in the muscle tissue.
Solution
Myofibrils
Q11. How is lymph different from blood?
Solution
Lymph does not contain a few proteins and erythrocytes which are
present in blood.
Q12. State the names of two common Indian earthworms.
Solution
Pheretima and Lumbricus
Q13. Draw a well-labelled diagram representing the excretory system of earthworm.
Solution
Excretory system of earthworm:


Q14. Name the regions in which the body of an earthworm is divided.
Solution
The body of an earthworm is divided into preclitellar, clitellar and
post-clitellar regions.
Q15. What are spermatophores?
Solution
Spermatophores are bundles of sperms glued together.
Q16. What is the function of antennae in cockroaches?
Solution
Antennae in cockroaches have sensory receptors which help in
monitoring the environment.
Q17. What is present at the junction of the midgut and hindgut? State its
function.
Solution
At the junction of the midgut and hindgut, a ring of 100-150 yellow
coloured Malpighian tubules are present. They absorb nitrogenous waste
products from the haemolymph and convert them into the excretory product,
i.e. uric acid.
Q18. Name the phylum and class to which frog belongs.
Solution
Frog belongs to the phylum Chordata and class Amphibia.
Q19. Name the class and phylum to which the cockroaches belong.
Solution
Cockroaches belong to the class Insecta of the phylum Arthropoda.
Q20. Identify the connective tissue:
(a) Provides a structural framework to the body
(b) Transports various substances in the human body
(c) Supports the framework for epithelium
(d) Attaches skeletal muscles to bones
Solution
(a) Provides structural framework to the body - Bones
(b) Transports various substances in the human body - Blood
(c) Supports the framework for epithelium - Areolar tissue
(d) Attaches skeletal muscles to bones - Tendons
Q21. Where is bile stored in the body of frog?
Solution
Bile is stored in the gall bladder in frogs.
Q22. How are earthworms traced in gardens?
Solution
Earthworms are traced by their faecal matter called worm casting in
gardens.
Q23. Write the name of organs where the smooth muscles are formed.
Solution
Smooth muscles are formed in blood vessels, intestines and stomach.
Q24. State the name of the space into which the blood vessels open in
cockroaches.
Solution
Haemocoel
Q25. Draw a labelled diagram of the open circulatory system of cockroach.
Solution

Q26. State the function of the muscular gizzard in earthworm.
Solution
The muscular gizzard in earthworm helps in grinding the soil particles and decaying leaves.
Q27. Name one epithelial tissue in which the nuclei are located at the base
of cells.
Solution
Columnar epithelium
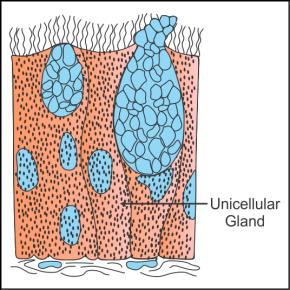
Q28. Represent diagrammatically:
(a) Unicellular glandular epithelium
(b) Cartilage tissue
Solution
(a) Unicellular glandular epithelium:
 (b) Cartilage tissue:
(b) Cartilage tissue:
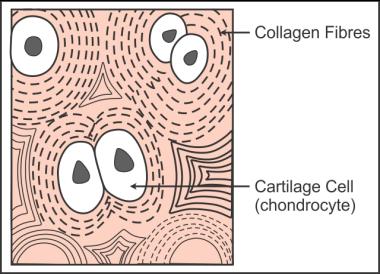
 (b) Cartilage tissue:
(b) Cartilage tissue:

Q29. Write the names of three junctions found in the epithelium.
Solution
Three junctions found in the epithelium are
1. Tight junctions
2. Adhering junctions
3. Gap junctions
Q30. Name the membrane which protects the eyes while the frog is in water.
Solution
The nictitating membrane protects the eyes while the frog is in water.
Q31. Name the connective tissue in which collagen is absent.
Solution
Blood
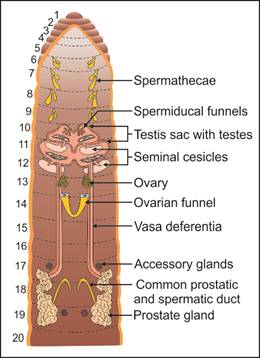
Q32. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the reproductive system of earthworm.
Solution
Reproductive system of earthworm:

Q33. What is clitellum?
Solution
Clitellum is a prominent dark band of glandular tissue which covers 14-16
segments in a mature earthworm.
Q34. How many times a nymph moults in order to attain the adult stage of
cockroach?
Solution
A nymph moults about 13 times to attain the adult stage of cockroach.
Q35. Write the scientific name for cockroach.
Solution
The scientific name for cockroach is Periplaneta americana.
Q36. Write the names of the mouthparts found in cockroach.
Solution
The mouthparts found in cockroach are a labrum, a pair of mandibles, a
pair of maxillae and a labium.
Q37. How many eggs are present in a single ootheca?
Solution
14 to 16 eggs are present in a singe ootheca.
Q38. Write the functions of bones.
Solution
Functions of bones:
They serve as the main tissue in providing a support
framework to the body.
They support and protect the softer tissues and
organs in the body.
The limb bones bear the weight of the body.
The limb bones interact with the skeletal
muscles attached to them to bring about movements in the body.
The bone marrow serves as the site of
production of blood cells.
(Write any four)
Q39. Describe the exoskeleton of cockroach.
Solution
In cockroach, the exoskeleton is hard, chitinous and brown in colour.
It is made of hardened plates called sclerites.
The sclerites present on the dorsal side are called tergites, and the ones present on the ventral side are sternites.
Tergites and sternites are joined to one another by a flexible, articular membrane called the arthrodial membrane.
Q40. Represent the mouth part of cockroach diagrammatically.
Solution
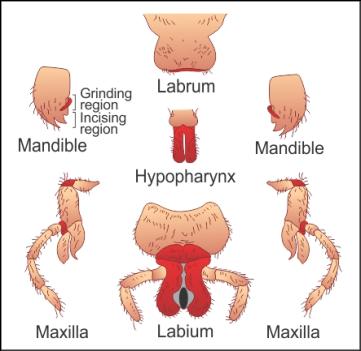
Comments
Post a Comment