Q1. In solutions of different pH, the structure of amino acids changes. Justify.
Solution
The -NH2 and -COOH groups of amino acids exhibit an ionisable nature. With a change in pH, these groups undergo ionisation. Hence, the structure of amino acid changes in solutions of different pH.
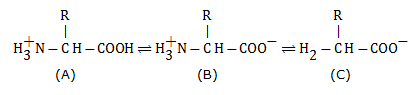
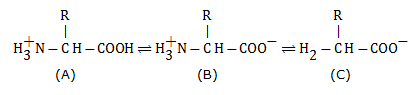
Q2. What is the transition state structure of substrate?
Solution
The transition state structure of the substrate is the structure when the substrate is bound to the enzyme before converting itself into a product.
Q3. What are proteins?
Solution
Proteins are polypeptides, i.e. macromolecules formed of a linear
chain of amino acids linked to each other by peptide bonds.
Q4. Classify the following into nitrogen bases, nucleosides and nucleotides:
Guanine
Adenosine
Thymidylic acid
Uridine
Solution
Nitrogenous Base
Nucleoside
Nucleotide
Guanine
Adenosine
Uridine
Thymidylic acid
Q5. Define a homopolymer.
Solution
It is a polymer when one type of unit (i.e. the monomer) is repeated
‘n’ number of times.
Q6. Give an example of a lectin.
Solution
Conconavalin A is a lectin (carbohydrate-binding protein) which is extracted from the jack-bean
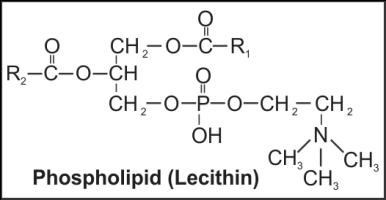
Q7. Give one example of phospholipid. Also draw its structure.
Solution
Lecithin

Q8. What is the energy currency in living organisms?
Solution
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency in living organisms.
Q9. Name the following:
20 carbon atom fatty acid
16 carbon atom fatty acid
Solution
Q10. How is a peptide bond formed?
Solution
When the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the
(-NH2) group of the next amino acid, a molecule of water is eliminated by the
process dehydration resulting in the formation of a peptide bond.
Q11. What is the other name given to
B-DNA?
Solution
The
other name given to B-DNA is the Watson-Crick model.
Q12. Name the protein which is most abundantly found in the biosphere.
Solution
Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO) is the most
abundantly found in the biosphere.
Q13. State the significance of the tertiary structure of proteins.
Solution
Significance of the tertiary structure of proteins:
1. It gives the
3-dimensional structure of proteins.
2. It is necessary for
many biological processes.
Q14. Describe the salient features of B-DNA.
Solution
Salient features of B-DNA are as follows:
The two strands of polynucleotides run anti-parallel.
The backbone of the double helical structure is formed by the sugar-phosphate-sugar chain.
The nitrogenous bases lie perpendicular to the backbone of the molecule. They lie on the inner side.
There is a complementary base pairing between two anti-parallel strands. Example: A pairs with T and G pairs with C. A and T are paired by the formation of two hydrogen bonds, and G and C are paired by the formation of three hydrogen bonds.
Each strand of DNA appears like a helical staircase.
Each step of the strand is represented by a pair of bases.
At each step, the strand turns 36°.
One full turn of the strand involves 10 base pairs.
The distance between two successive sugar molecules is 3.4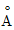 .
.
 .
.
Q15. Give any two examples of aromatic amino acids.
Solution
Examples of aromatic amino acids are tryptophan and tyrosine.
Q16. Give an example of anabolic pathway.
Solution
Example of the anabolic pathway: Formation of cholesterol from acetic acid
Q17. What is a chemical reaction?
Solution
The process of transformation of a substance in which old bonds are
broken and new bonds are formed is called a chemical reaction.
Q18. State the number of hydrogen bonds present between the following base pairs:
Adenine and Thymine
Guanine and Cytosine
Solution
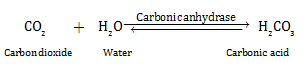
Q19. The rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction is tremendously higher than the rate of uncatalysed reactions. Explain by an example.
Solution
The rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction is tremendously higher than the rate of uncatalysed reactions. Example:
When carbon dioxide and water react with each other in the absence of any enzyme, only 200 molecules of carbonic acid are formed in an hour.
When the same reaction occurs in the presence of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, 600,000 molecules of carbonic acids are formed every second.

Q20. Where are phospholipids found in animal and plant cells?
Solution
Phospholipids are found in the cell membrane of animal and plant cells.
Q21. Define cofactors.
Solution
Cofactors are the non-protein constituents which bind to the enzyme to
make the enzyme catalytically active.
Q22. Name the processes by which macromolecules form/break down
from/into micromolecule monomers.
Solution
The process is condensation/hydrolysis.
The common macromolecules are polysaccharides, proteins
and nucleic acids.
Q23. Define biomolecules.
Solution
All the carbon compounds which are obtained from living tissues are
called biomolecules.
Q24. What component of amino acids gives them their unique
properties?
Solution
The side carbon chain or ring joined to the central
α-carbon on the fourth side.
Q25. Describe the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Also write the symbolic equation of the formation of the enzyme-product complex.
Solution
The catalytic cycle of an enzyme action occurs in the following steps:
The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme.
The binding of the substrate induces a change in the shape of the enzyme molecule, and the substrate firms itself more tightly into the active site.
The active site results in the breaking of the chemical bonds of the substrate, resulting in the formation of a new enzyme-product complex.
The enzyme molecule releases the product of the reaction and becomes free again to receive the new substrate molecule.
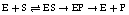
Q26. How many amino acids exist in the biosphere?
Solution
20 amino acids exist in the biosphere.
Q27. Name two alkaloids and flavonoids.
Solution
Alkaloids:
Morphine, codeine
Flavonoids:
Quercetin, apigenin
Q28. Give one example of the role of the prosthetic group as a cofactor.
Solution
Peroxidase and catalase catalyse the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide
into water and oxygen.
Haem is a prosthetic group. It is part of the active site of enzymes and
activates the two mentioned enzymes to catalyse the process.
Q29. Explain how metal ions activate enzyme action. Give one example.
Solution
Metal ions form coordinate bonds with the side chains at the active site. At the same time, they form one or more coordinate bonds with the substrate. Example: Zinc acts as a cofactor for the proteolytic enzyme carboxypeptidase.
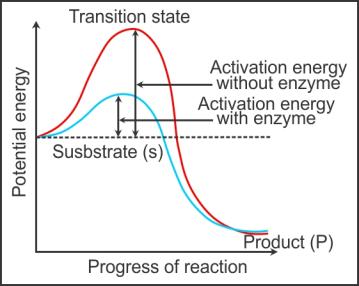
Q30. Draw a graph depicting the concept of activation energy during an
enzyme catalysed reaction.
Solution
Q31. What is a nucleotide?
Solution
A nucleotide is the combination of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar
and a phosphate group esterified with the pentose sugar.
Q32. Explain the mechanism of enzyme inhibition.
Solution
An inhibitor usually closely resembles the substrate in its molecular
structure.
Due to structural resemblance, the inhibitor competes with the
substrate for the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Hence, the substrate cannot bind to the enzyme which results in a decline
of enzyme action.
Q33. Name the bond which links amino acids in a polypeptide.
Solution
The peptide bond links amino acids in a polypeptide.
Q34. Define activation energy.
Solution
The difference in average energy content of a substrate from its
transition state is called activation energy.
Q35. What are ribozymes?
Solution
Nucleic acids which act like enzymes are called ribozymes.
Q36. State any one property of amino acids.
Solution
-NH2 and -COOH groups of amino acids exhibit the ionisable
nature.
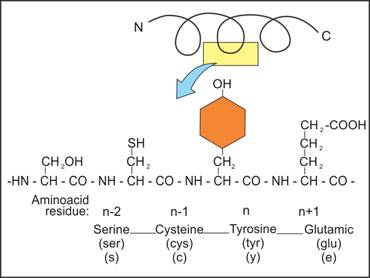
Q37. Draw a primary structure of a hypothetical protein.
Solution
Primary Structure of a Hypothetical
Protein:

Q38. Define optimum temperature.
Solution
The temperature at which an enzyme shows its highest activity is
called optimum temperature.
Q39. Name the most abundant protein found in the animal world.
Solution
Collagen
Q40. Name any two nucleotides.
Solution
Guanylic acid
Cytidylic acid
Comments
Post a Comment